Article
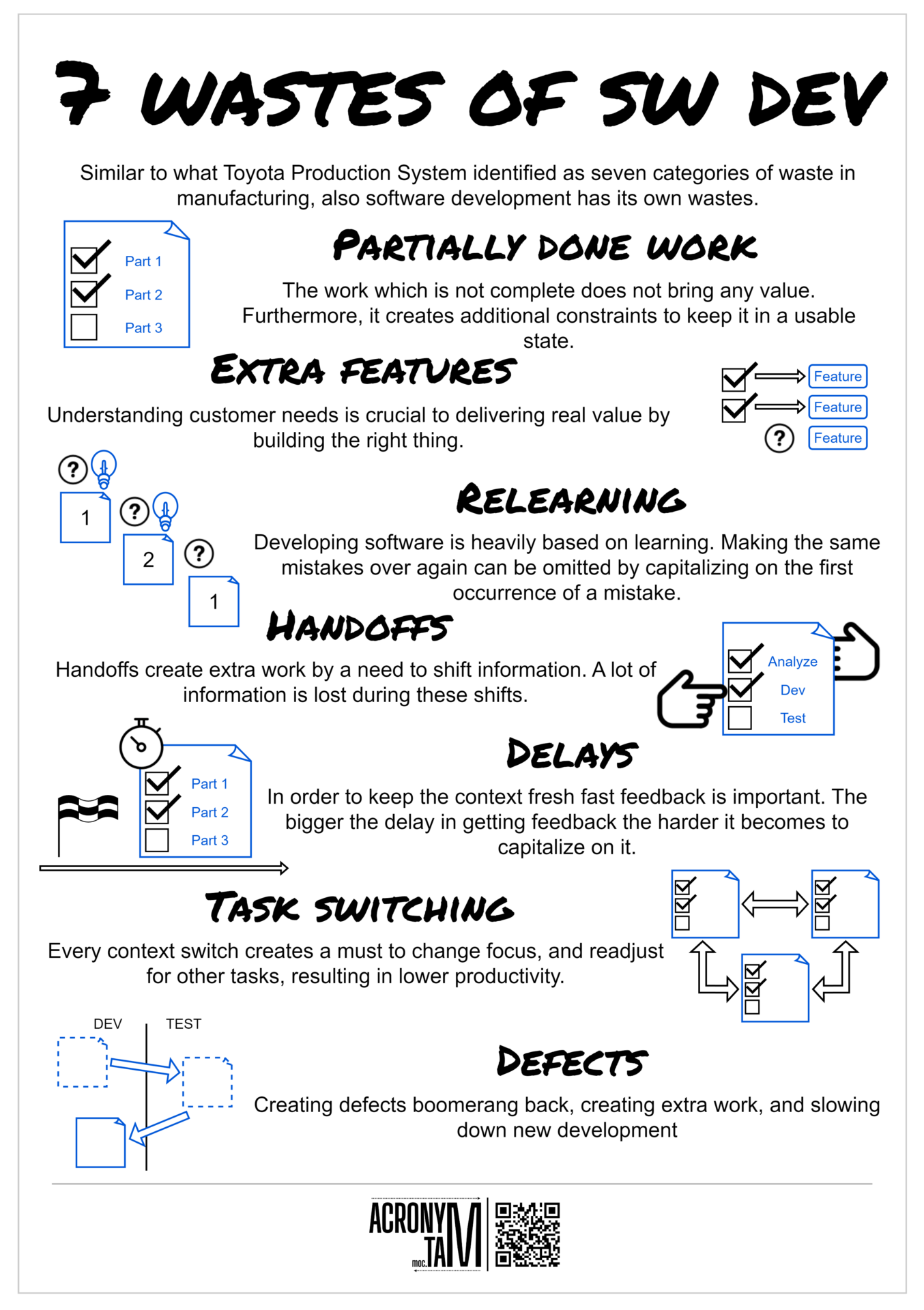
Similar to what Toyota Production System identified as seven categories of waste in manufacturing, also software development has its own wastes.
Partially done work
The work which is not complete does not bring any value. Furthermore, it creates additional constraints to keep it in a usable state.
Extra features
Understanding customer needs is crucial to delivering real value by building the right thing.
Relearning
Developing software is heavily based on learning. Making the same mistakes over again can be omitted by capitalizing on the first occurrence of a mistake.
Handoffs
Handoffs create extra work by a need to shift information. A lot of information is lost during these shifts.
Delays
In order to keep the context fresh fast feedback is important. The bigger the delay in getting feedback the harder it becomes to capitalize on it.
Task switching
Every context switch creates a must to change focus, and readjust for other tasks, resulting in lower productivity.
Defects
Creating defects boomerang back, creating extra work, and slowing down new development