Maslow’s Hierarchy Of Needs
Article
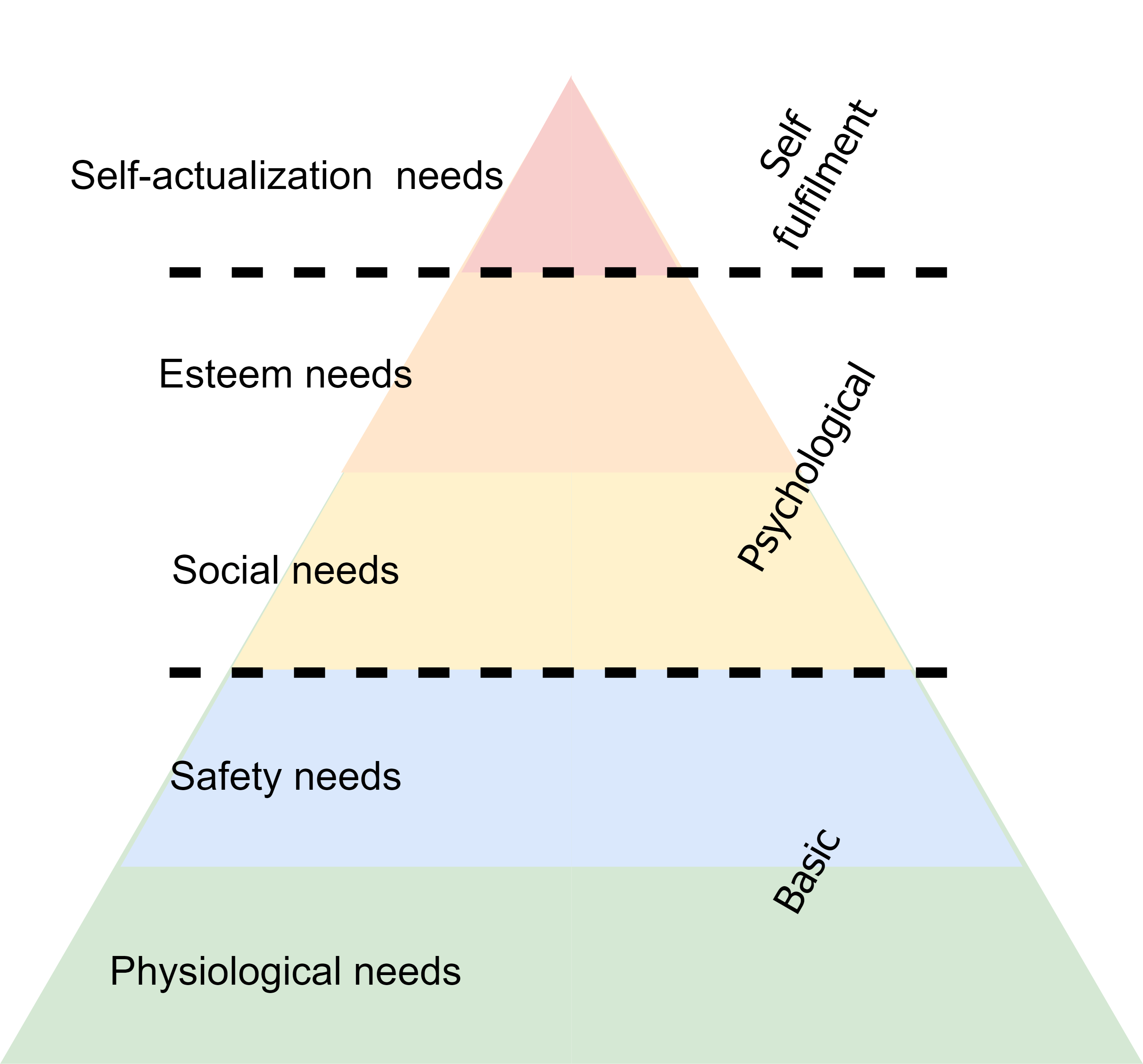
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs outlines the link between basic human needs and desires, emphasizing that survival needs must be met before higher needs. Despite the hierarchical structure, the sequence is flexible, with esteem occasionally surpassing love, and individuals can self-actualize despite poverty. Human behaviors are complex, often motivated by a combination of needs simultaneously. Going up the hierarchy, the focus shifts from physiological and short-term requirements to more psychological and long-term aspirations. Maslow’s pyramid helps to identify target needs, humanize personas, and align quantitative data with qualitative needs that are applicable in diverse fields, including workplace motivation, education, counseling, and nursing.
Physiological needs
Biological requirements essential for human survival, e.g. air, food, drink, shelter, clothing, warmth, sex, and sleep.
Safety needs
Fulfillment is found in life’s order, predictability, and control, provided by family and society, contributing to emotional and financial security.
Social needs
Emotional needs include interpersonal relationships, like friendship, intimacy, trust, acceptance, and the exchange of affection through affiliating, connectedness, and group belonging.
Esteem needs
Esteem needs represent a desire to be accepted and valued by others. They are split into two subcategories: 1. esteem for oneself (dignity, achievement, mastery, independence) and 2. the desire for reputation or respect from others (status, prestige).
Self-actualization
People are striving to reach the limits of an individual realizing a person’s potential, self-fulfillment, seeking personal growth, and peak experiences, which is difficult to achieve consistently.