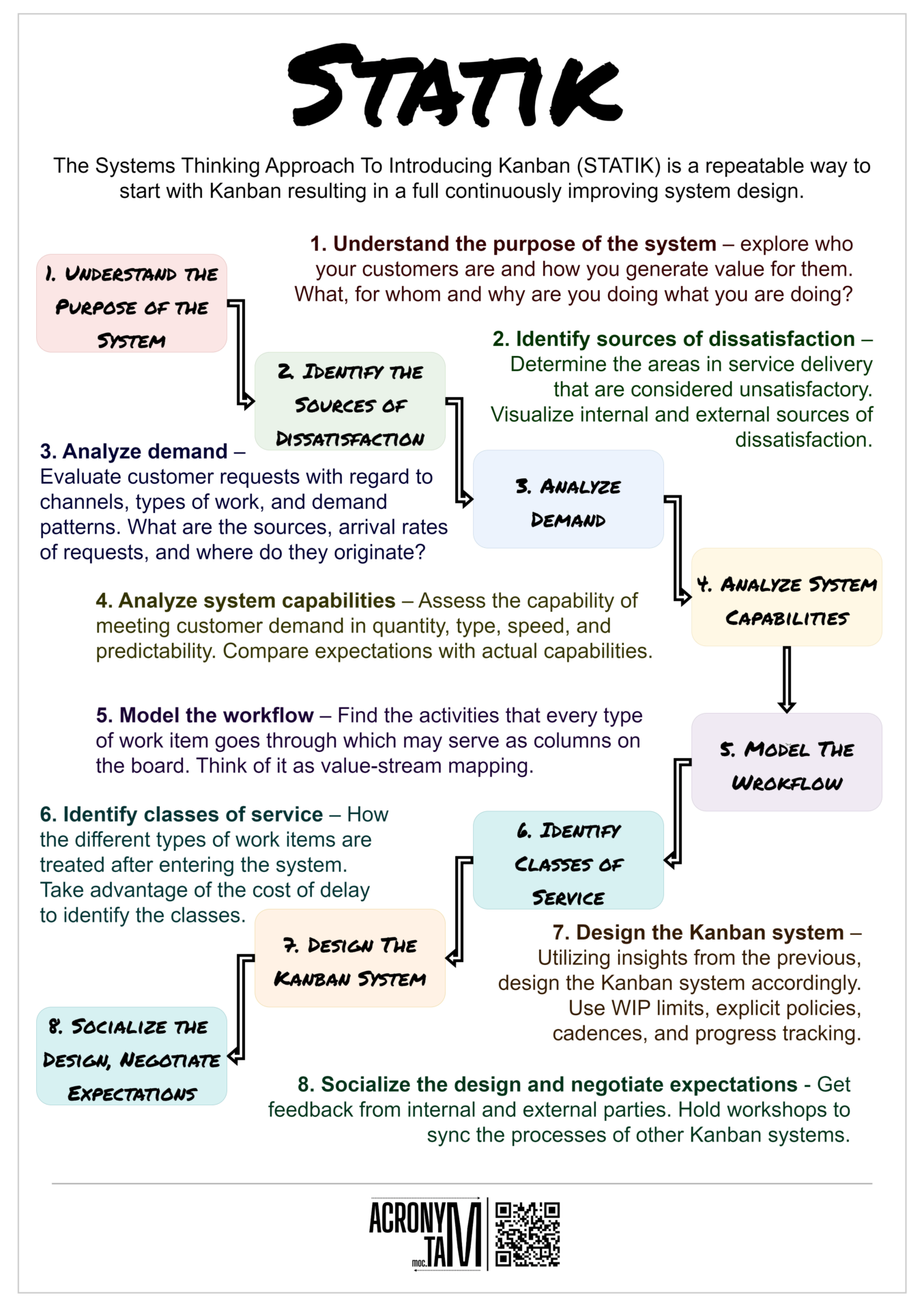
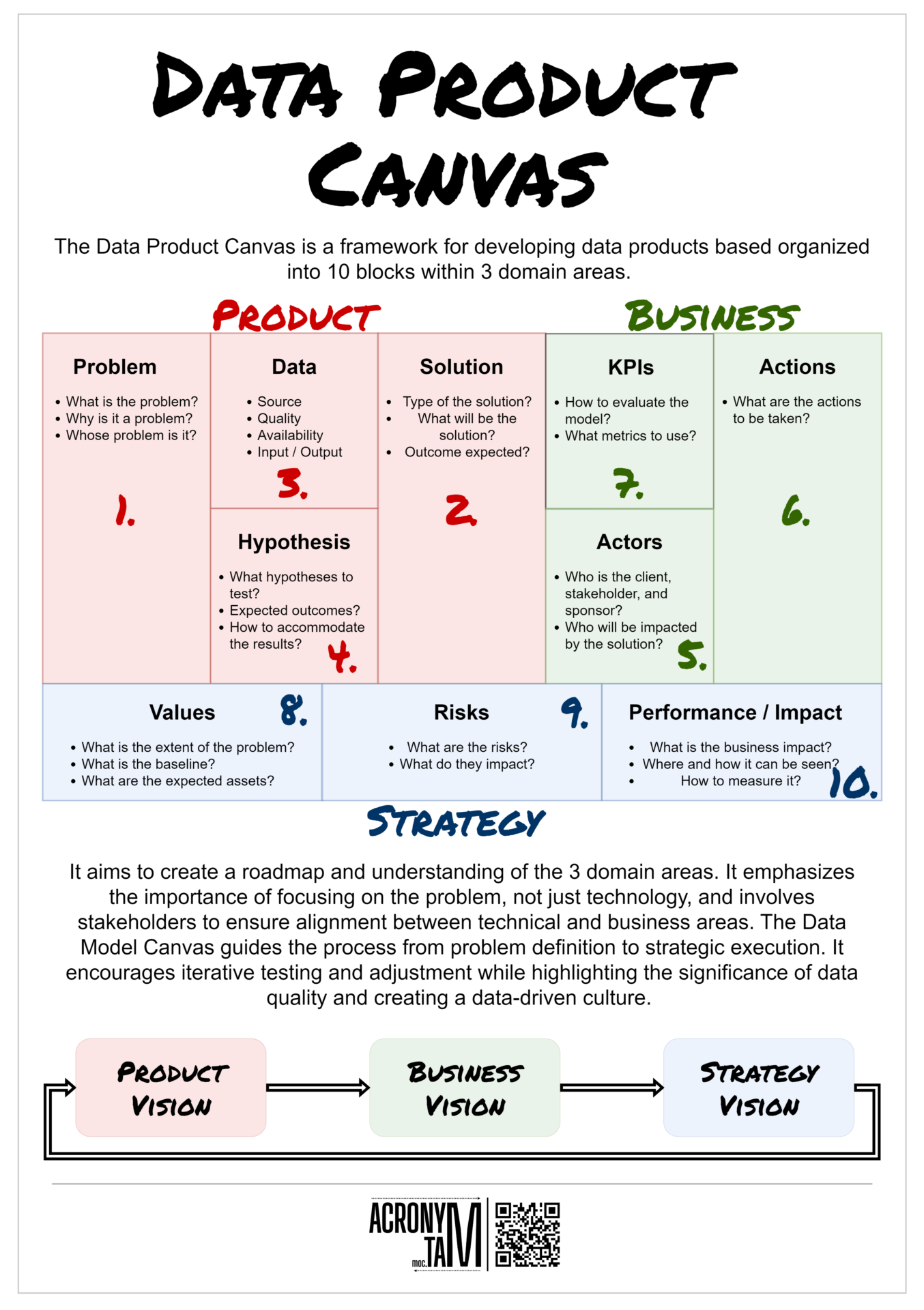
Article
The AIDAOR model is a hierarchical model, where a persona moves through a series of cognitive steps before and after making a purchase decision. Compared to the AIDA model the AIDAOR is extended with phases after the purchase decision.
Attention / Awarness
The first step is to attract consumers by creating awareness or affiliation for a service, category, product, or brand. For example, ran a PR campaign in advance.
Interest
Increase potential customer interest by learning about the benefits and advantages of the product. For example, direct mail campaign to offer a free consultation.
Desire
Make the consumer develop an ’emotional connection’. The transition from ‘liking’ to ‘wanting’. For example, local launch events which were previously advertised.
Action
The consumer initiates an action (CTA), the next step. Purchase intention, shopping around, engaging in a trial, etc. Call to purchase on social media sites or a website.
Onboarding
The consumer gets an initial reward. Things needed for the consumer to become a regular. Usage of all the product capabilities like finding related users, integrations, etc.
Retention
Ensuring the consumer stays happy and active. Increasing satisfaction of the consumer over time, long-term monetization, consumer growth, and sharing.