Article
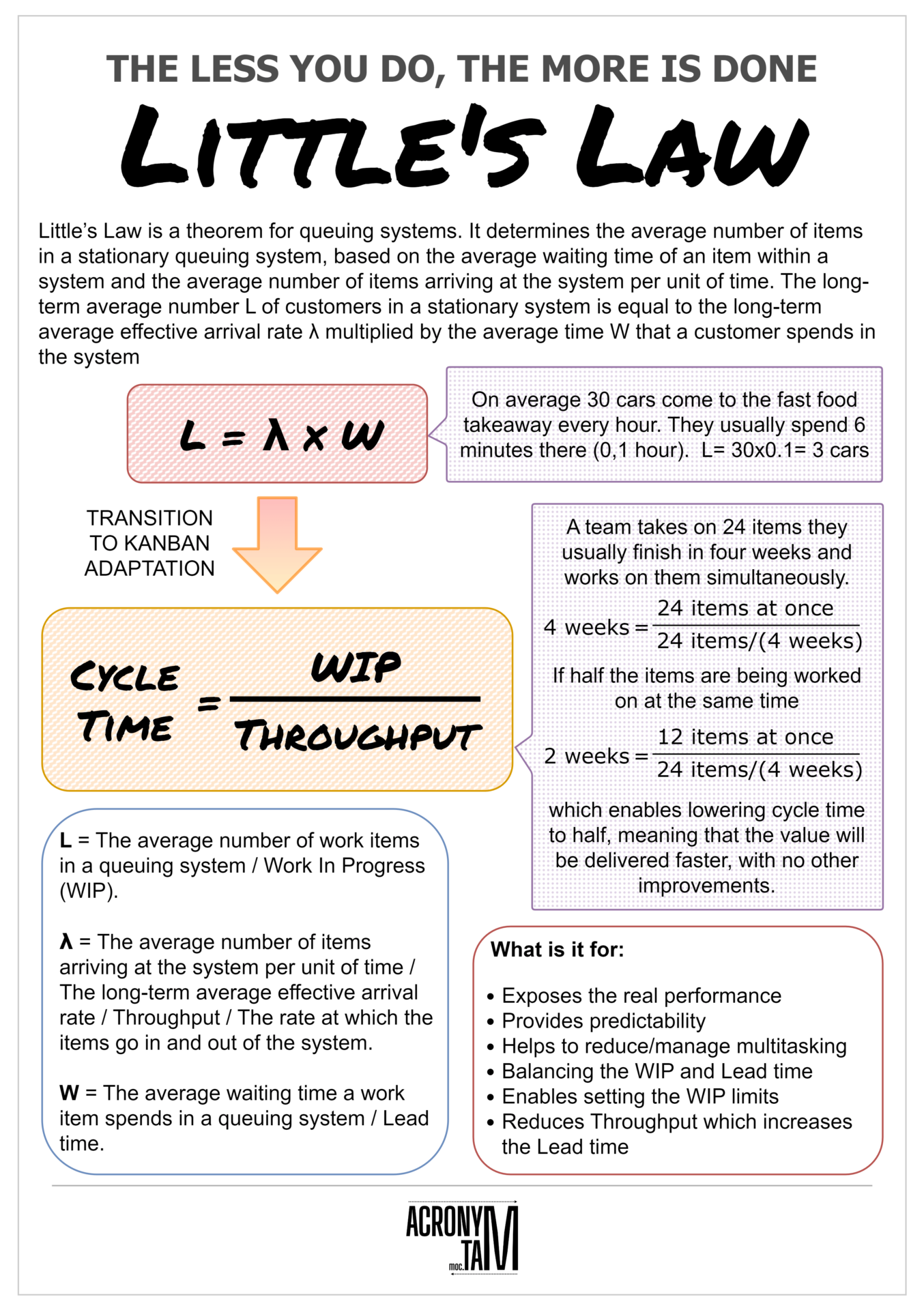
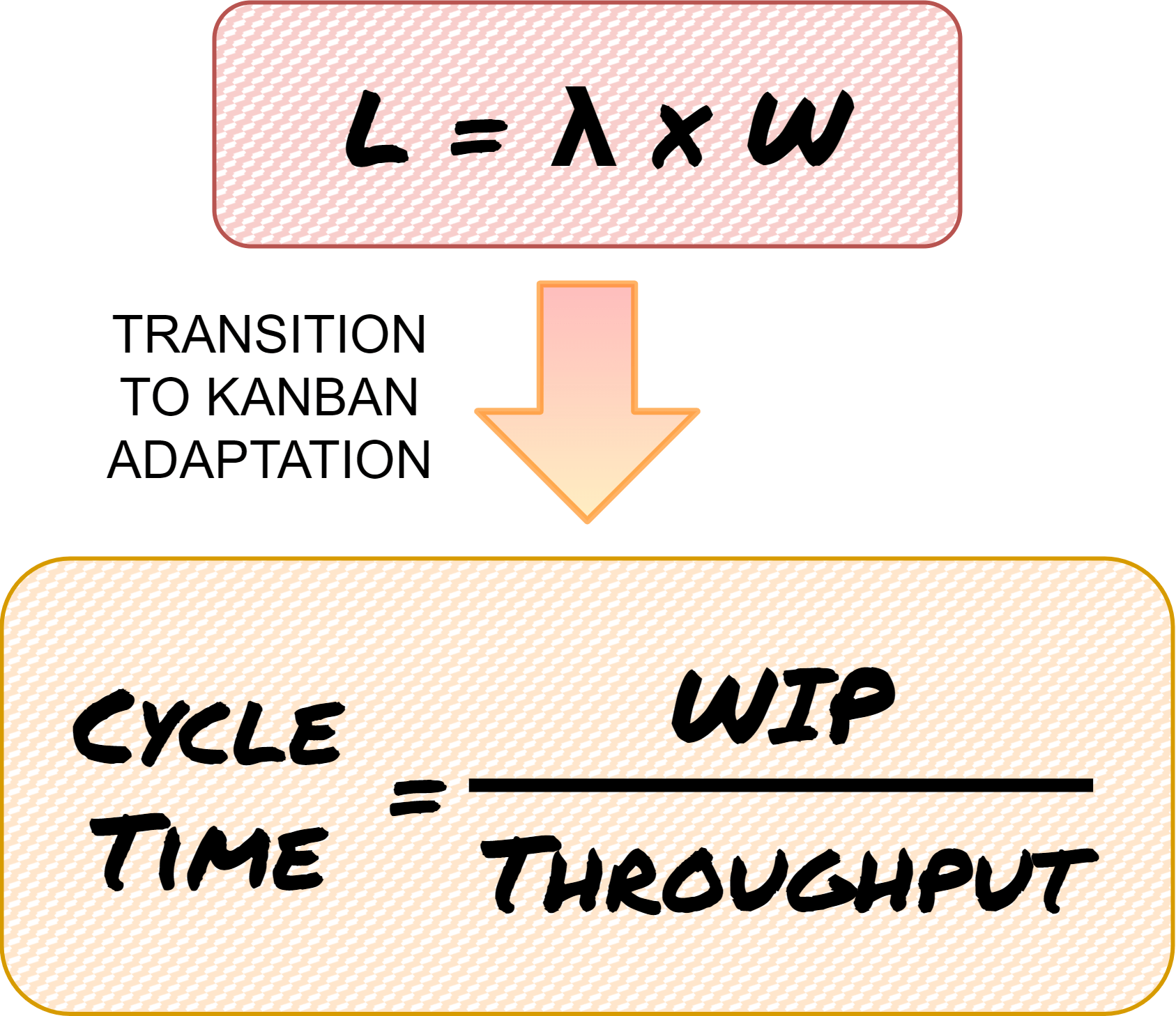
Little’s Law is a theorem for queuing systems. It determines the average number of items in a stationary queuing system, based on the average waiting time of an item within a system and the average number of items arriving at the system per unit of time. The long-term average number L of customers in a stationary system is equal to the long-term average effective arrival rate λ multiplied by the average time W that a customer spends in the system
Little’s law variables:
- L = The average number of work items in a queuing system / Work In Progress (WIP).
- λ = The average number of items arriving at the system per unit of time / The long-term average effective arrival rate / Throughput / The rate at which the items go in and out of the system.
- W = The average waiting time a work item spends in a queuing system / Lead time.
Example 1
On average 30 cars come to the fast food takeaway every hour. They usually spend 6 minutes there (0,1 hour). L= 30×0.1= 3 cars are usually in the line.
Example 2
A team takes on 24 items they usually finish in four weeks and works on them simultaneously.
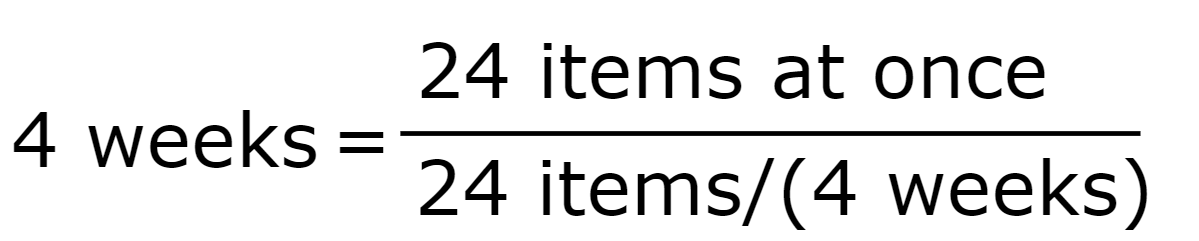
but if half the items are being worked on at the same time
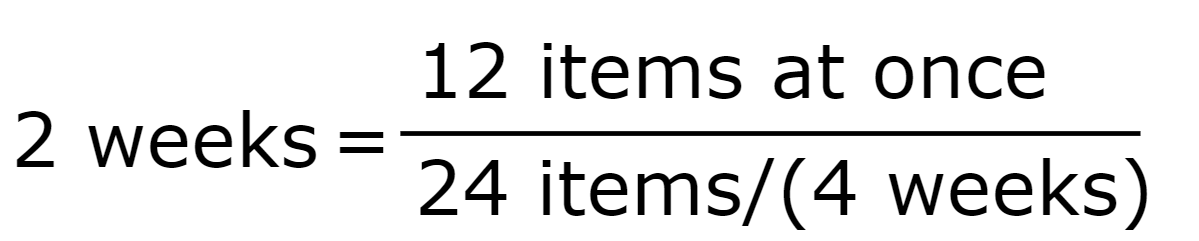
which enables lowering cycle time to half, meaning that the value will be delivered faster, with no other improvements.
What is it for:
- Exposes the real performance
- Provides predictability
- Helps to reduce/manage multitasking
- Helps to balance the work in progress and Lead time
- Enables setting the WIP limits
- Reduces Throughput which increases the Lead time