Article
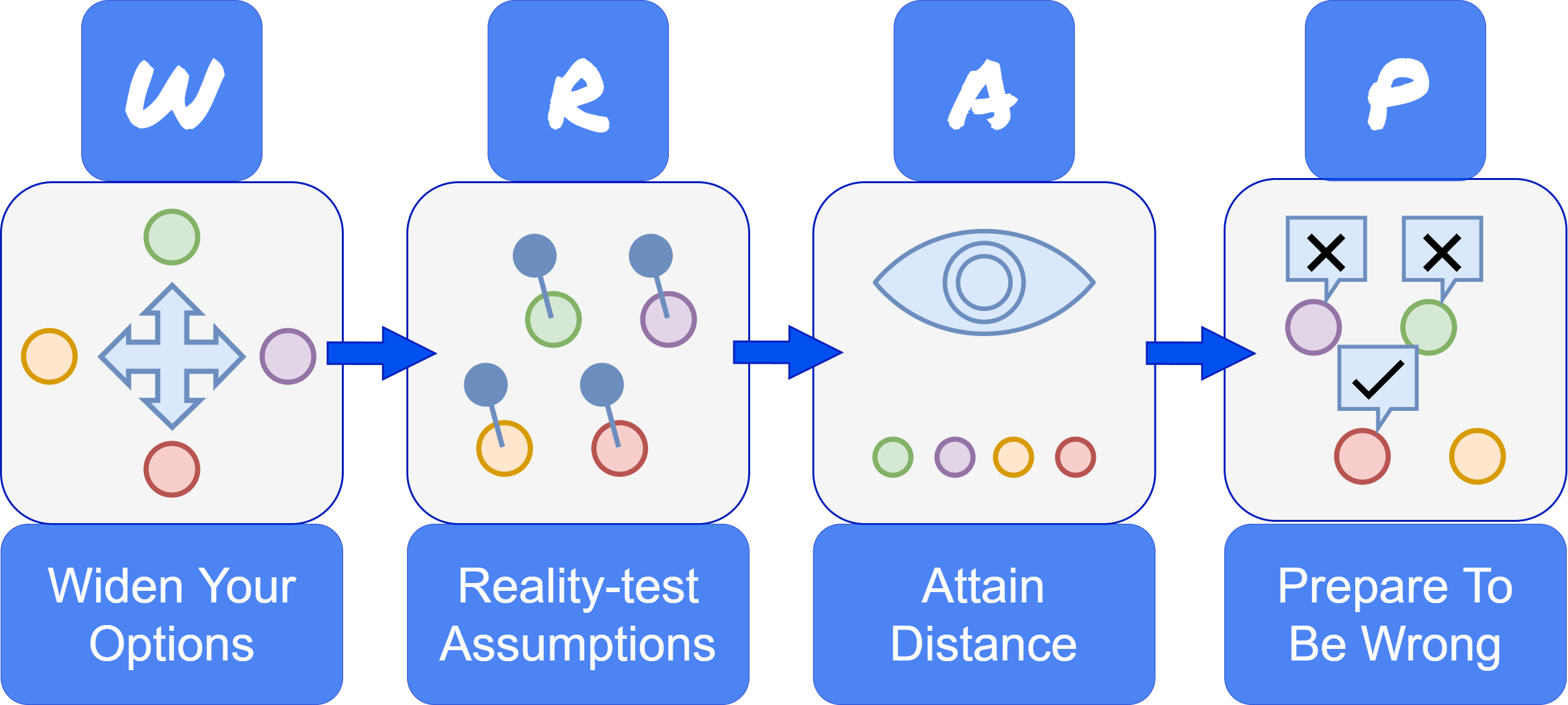
Decision-making is an important everyday process. When making important choices we need to be aware of and avoid decision-making biases like Outcome Bias, Cognitive Bias and Confirmation Bias. To be able to do that we can employ the WRAP model for decision-making.
Widen Your Frame
Consider alternative solutions for the problem to avoid narrow framing. Think about opportunity costs, multitrack, explore analogies or good practices.
Reality Test Your Assumptions
Fight confirmation bias by testing and running experiments. Look into details, consider outside and inside views, seek additional data, play the devil’s advocate.
Attain distance Before Deciding
Eliminate short-term emotions by shifting perspective. Postpone the decision, pretend to give advice to a friend, or use the 10 minutes/ 10 months / 10 years rule.
Prepare to Be Wrong
Expect both to be wrong or right, considering the VUCA world. Do not overestimate your ability to predict the future, be prepared to explore the outcomes as they are.