Article
MVP Types
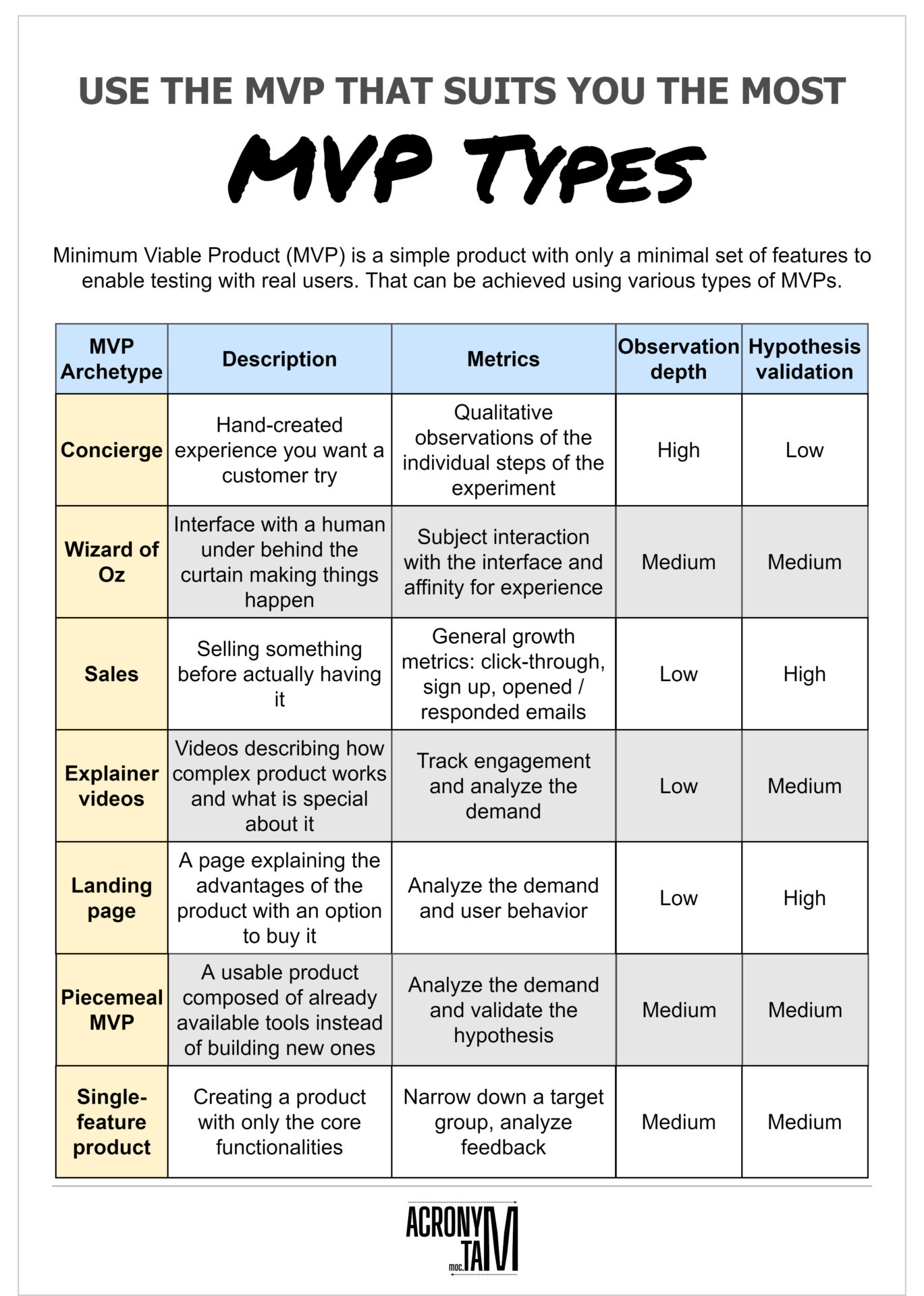
Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a simple product with only a minimal set of features to enable testing with real users. That can be achieved using various types of MVPs.| MVP Archetype | Description | Metrics | Observation Depth | Hypothesis Validation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concierge | Hand-created experience you want a customer try | Qualitative observations of the individual steps of the experiment | High | Low |
| Wizard of Oz | Interface with a human under behind the curtain making things happen | Subject interaction with the interface and affinity for experience | Medium | Medium |
| Sales | Selling something before actually having it | General growth metrics: click-through, sign up, opened / responded emails | Low | High |
| Explainer video | Videos describing how complex product works and what is special about it | Track engagement and analyze the demand | Low | Medium |
| Landing page | Landing page explaining the advantages of the product with an option to buy it | Analyze the demand and user behavior | Low | High |
| Piecemeal MVP | A usable product composed of already available tools instead of building new ones | Analyze the demand and validate the hypothesis | Medium | Medium |
| Single-feature product | Creating a product with only the core functionalities | Narrow down a target group, analyze feedback | Medium | Medium |