Article
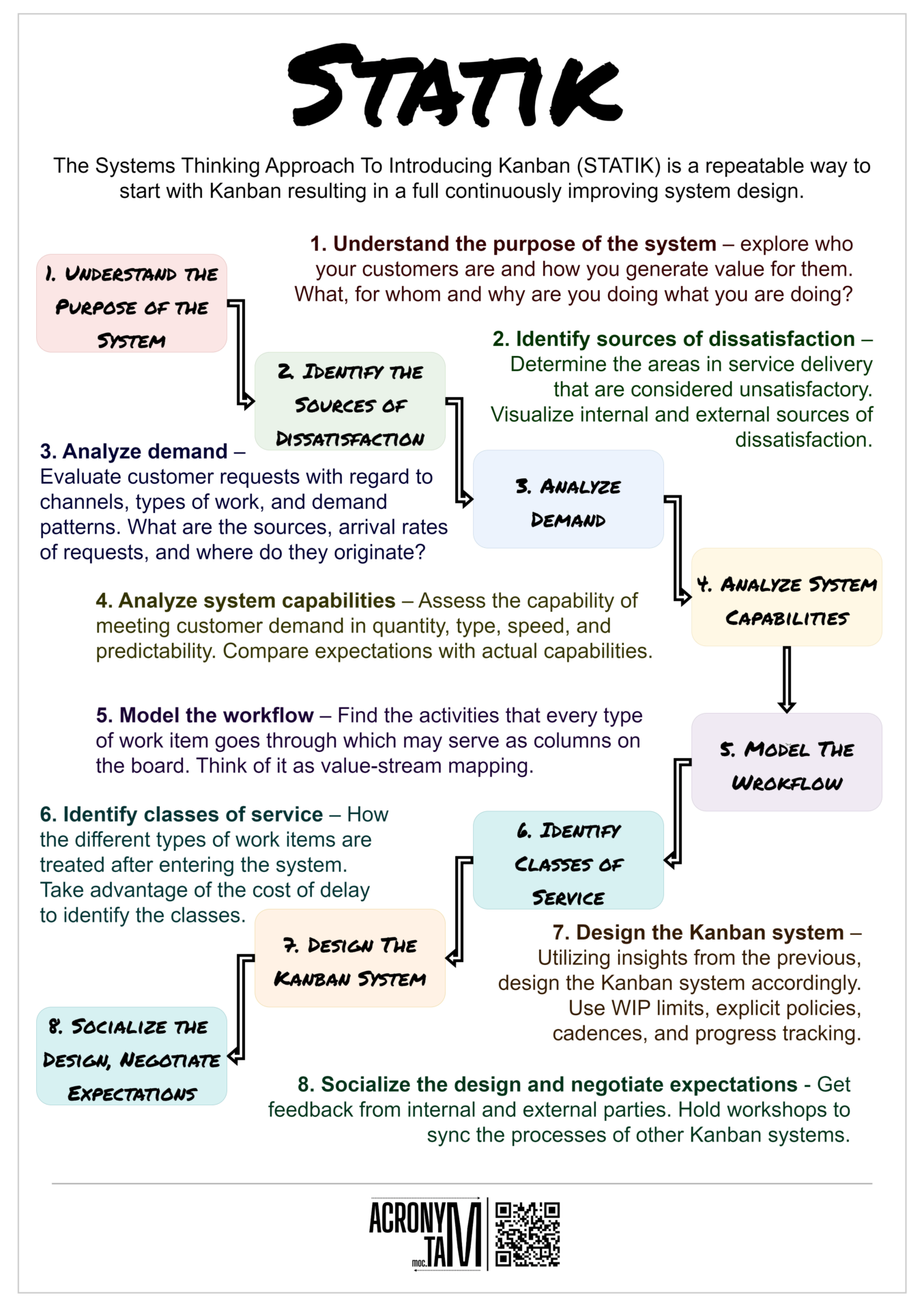
DMAIC Improvement Cycle
DMAIC is a data-driven process improvement cycle. It is based on the Scientific Method. DMAIC consists of five interconnected steps: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It is associated with Six Sigma but can be used also in a different context.
Define
The first step must provide a clear definition of the problem to be fixed, what is the scope, the goals to be achieved. Who are the stakeholders and how they are affected by the problem.
Measure
Providing a better insight into the problem by measuring the data in the process. Based on the data a baseline for measuring has to be set in order to track the changes. Collect the data from more sources.
Analyze
Based on the measurements the causes of problems need to be identified and tested. The analysis leads to identifying opportunities for improvement and how to achieve them.
Improve
The implementation of improvements resulting from analysis to the benefit of the project. These improvements are measured and compared to the baseline data from the Measure phase.
Control
Stabilize and quantify the impact of the improvements. A monitoring plan can be created. The final step of the DMAIC cycle before you can start again to address upcoming issues.