Article
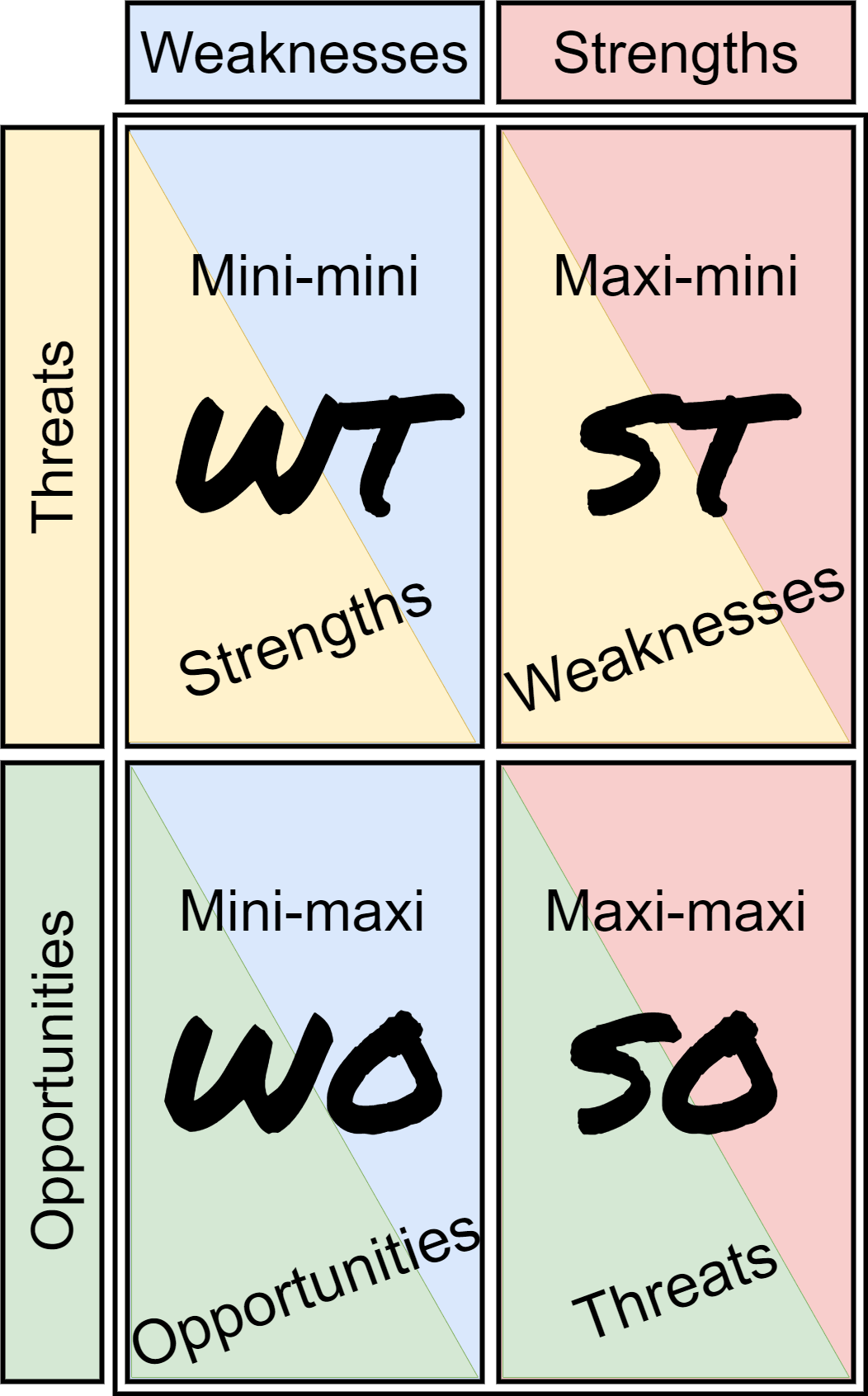
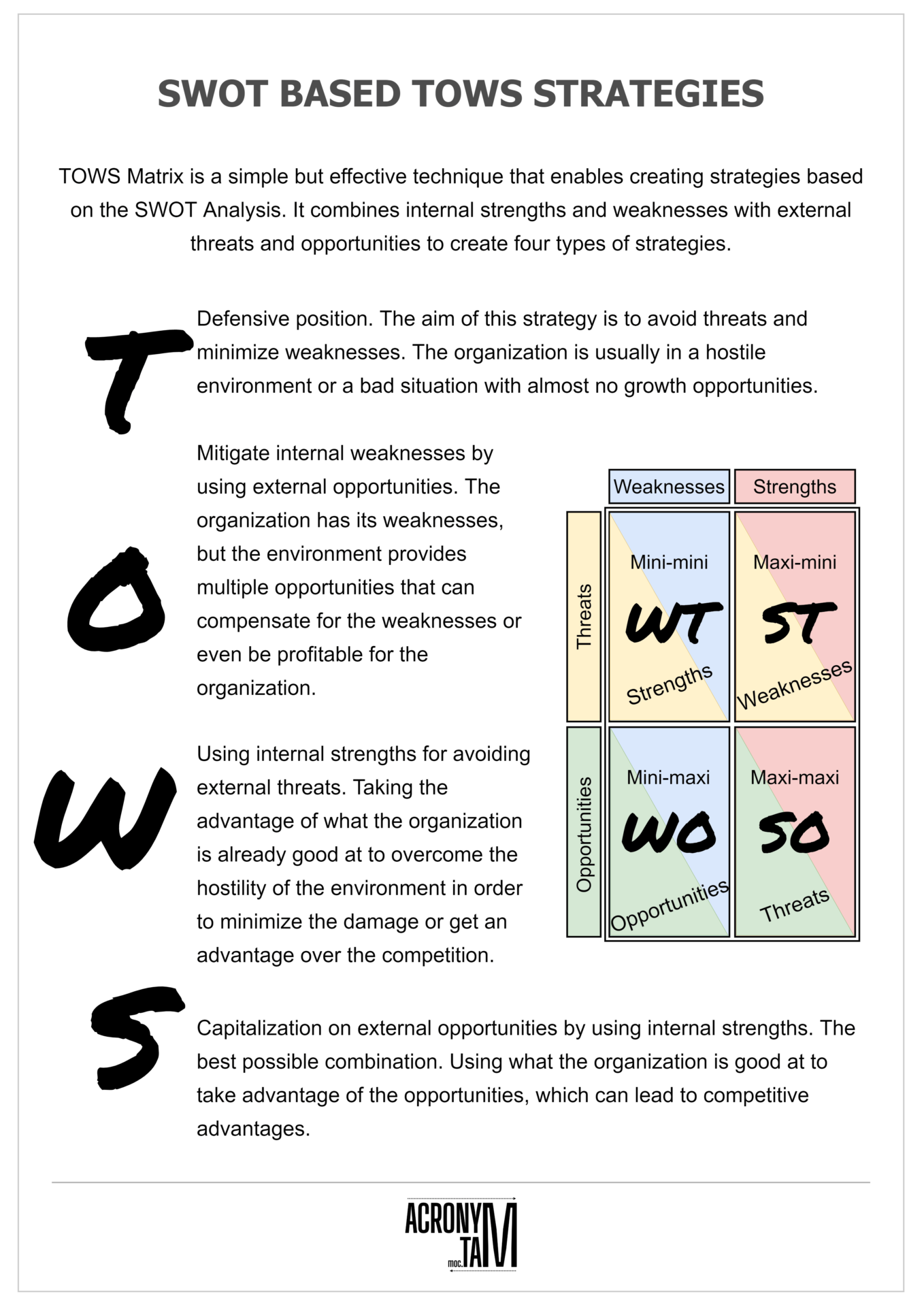
TOWS Analysis
TOWS Analysis is a simple but effective technique that enables creating strategies based on the SWOT Analysis. It combines internal strengths and weaknesses with external threats and opportunities to create four types of strategies.
WT Mini-mini
Defensive position. The aim of this strategy is to avoid threats and minimize weaknesses. The organization is usually in a hostile environment or a bad situation with almost no growth opportunities.
WO Mini-maxi
Mitigate internal weaknesses by using external opportunities. The organization has its weaknesses, but the environment provides multiple opportunities to compensate for the weaknesses or even be profitable for the organization.
ST Maxi-mini
Using internal strengths for avoiding external threats. Taking the advantage of what the organization is already good at to overcome the hostility of the environment in order to minimize the damage or get an advantage over the competition.
SO Maxi-maxi
Capitalization on external opportunities by using internal strengths. The best possible combination. Using what the organization is good at to take advantage of the opportunities leads to competitive advantages.