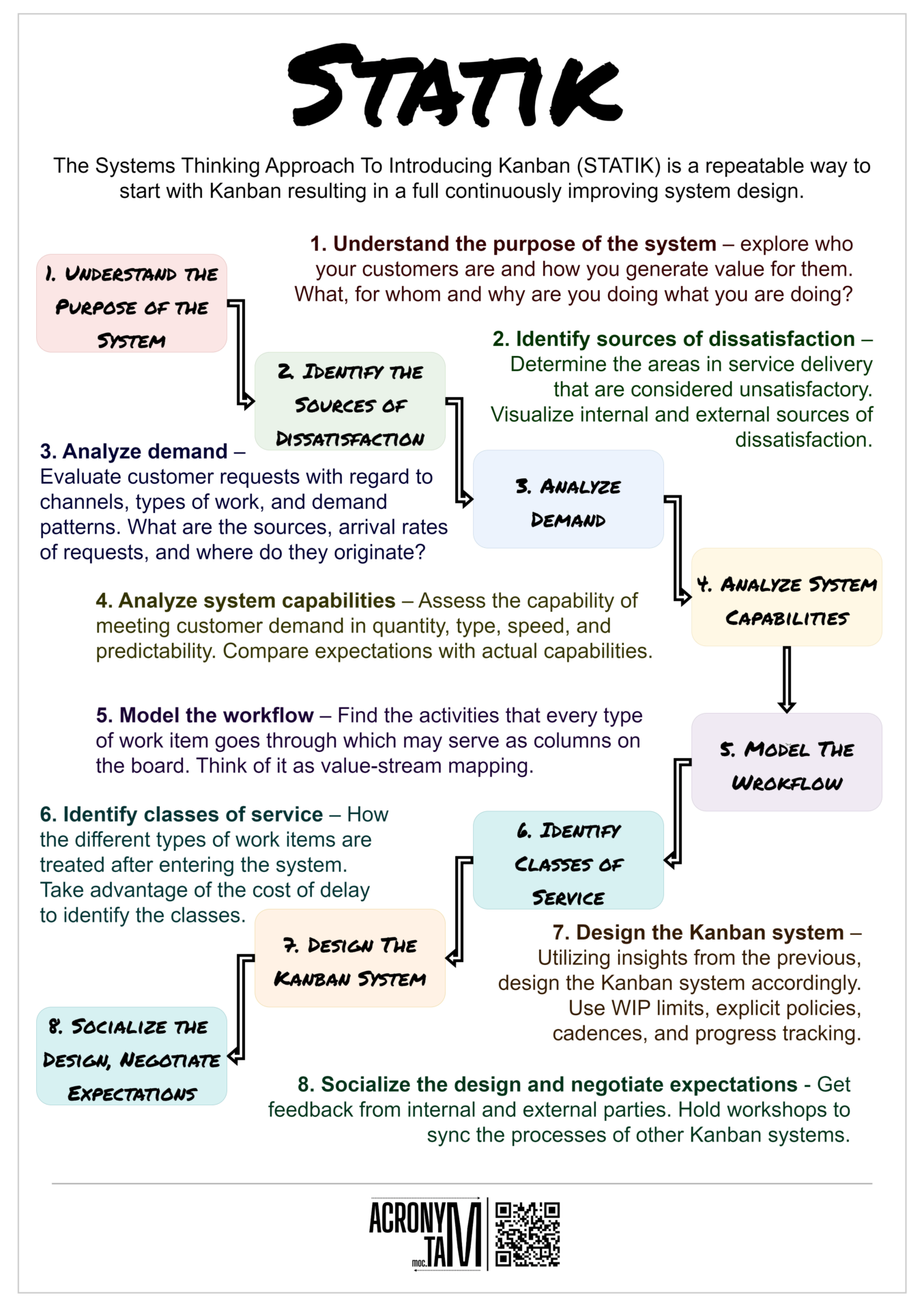
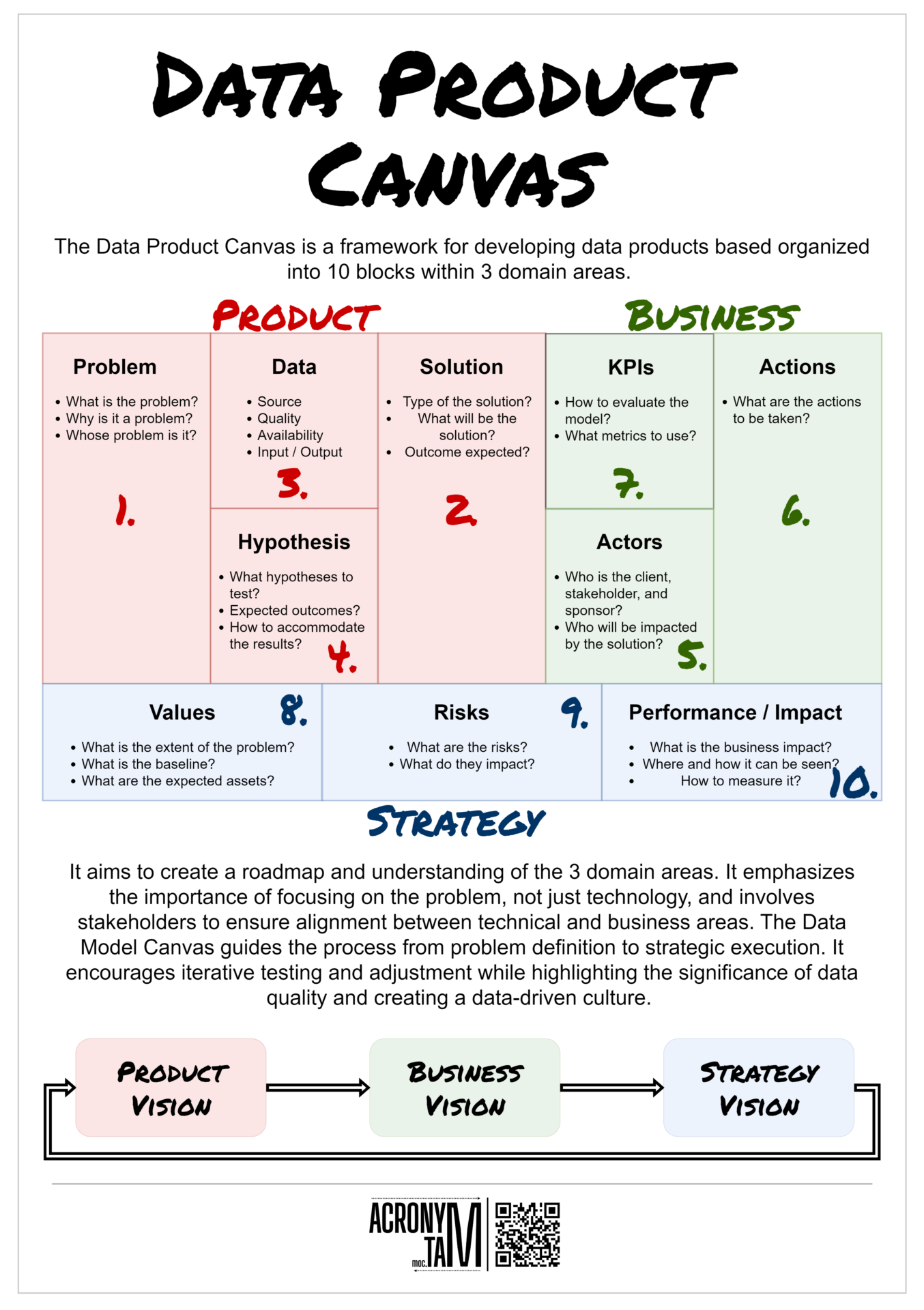
Article
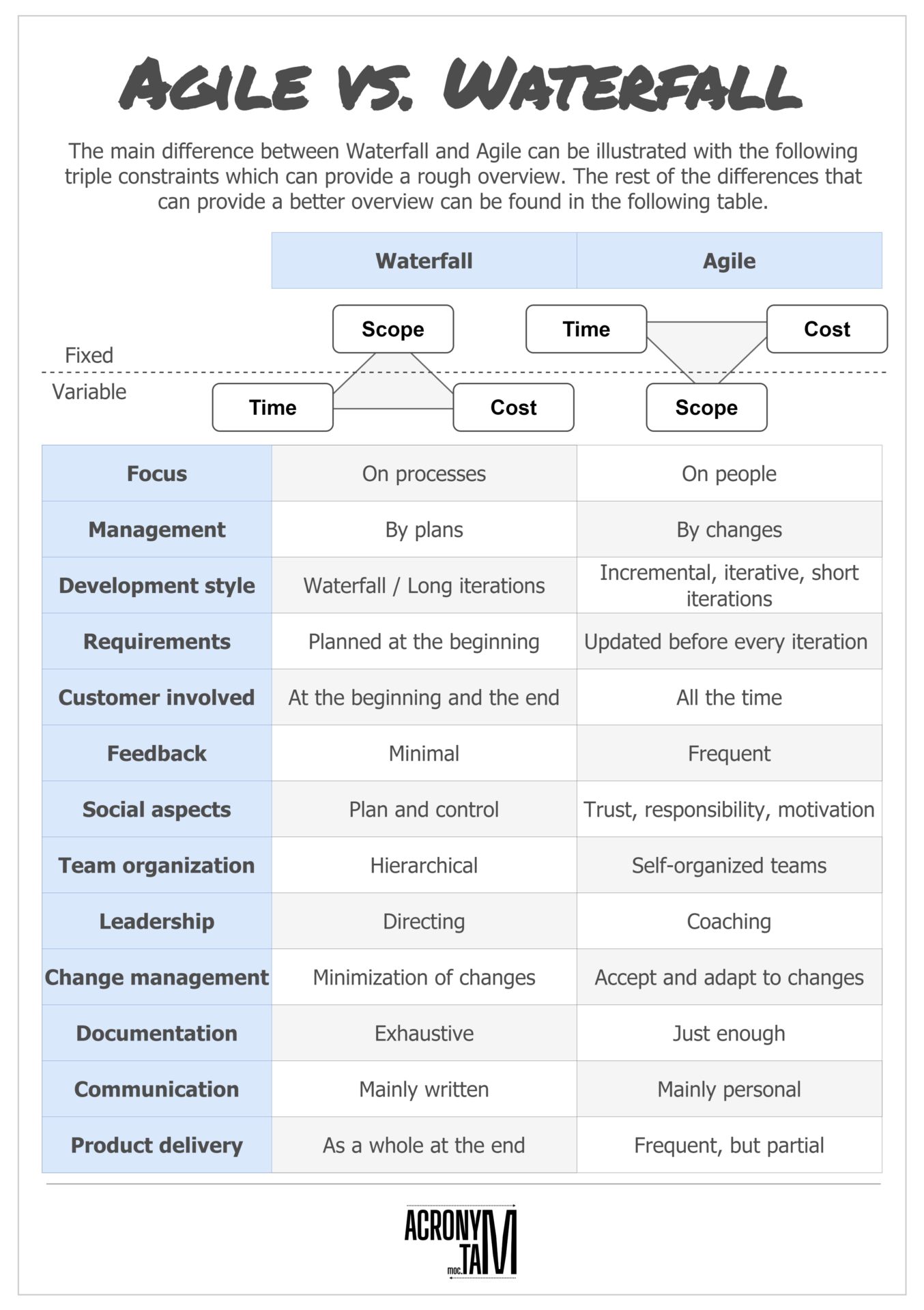
Agile vs Waterfall
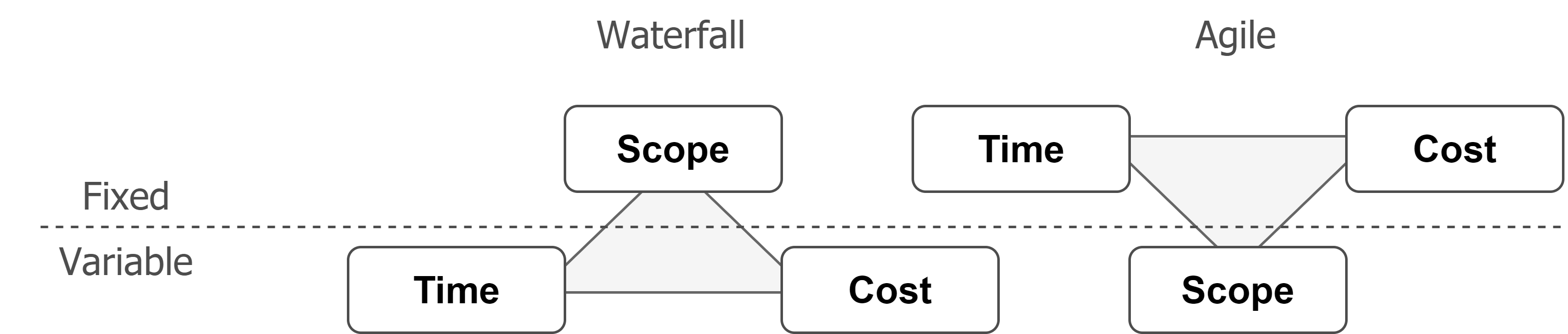
The main difference between Waterfall and Agile can be illustrated with the following triple constraints which can provide a rough overview. The rest of the differences that can provide a better overview can be found in the following table.
| Aspect / Approach | Waterfall | Agile |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | On processes | On people |
| Management | By plans | By changes |
| Development Style | Waterfall/ Long iterations | Incremental, iterative short iterations |
| Requirements | Planned at the beginning | Updated before every iteration |
| Customer involved | At the beginning and the end | All the time |
| Feedback | Minimal | Frequent |
| Social aspects | Plan and control | Trust, responsibility, motivation |
| Team organization | Hierarchical | Self-organized teams |
| Leadership | Directing | Coaching |
| Change management | Minimization of changes | Accept and adapt to changes |
| Documentation | Exhaustive | Just enough |
| Communication | Mainly written | Mainly personal |
| Product delivery | As a whole at the end | Frequent, but partial |