Article
Scrum Sprint Planning
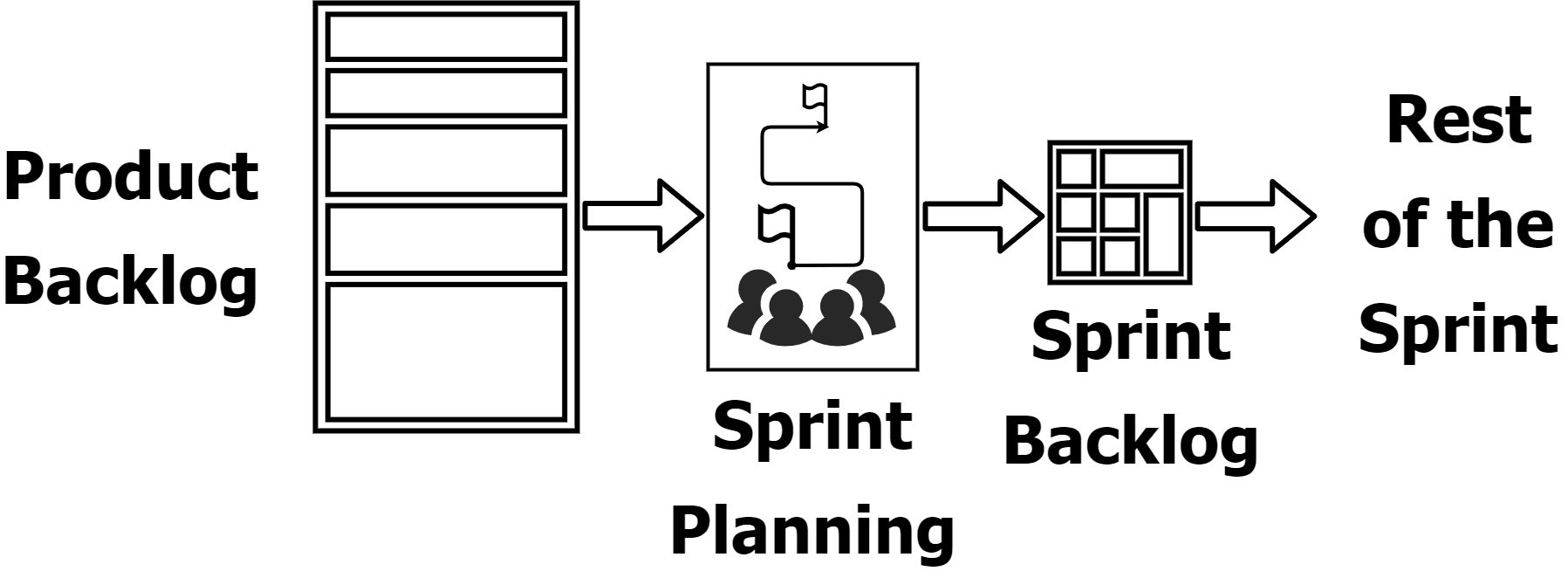
Scrum Sprint planning starts the sprint by choosing work for the sprint. The Scrum team participates to figure out, estimate and plan what needs to be done in the sprint. Time-box is 8 hours, for one month Sprint. The outcome is a Sprint Backlog which is composed of The Sprint Goal, the Product Backlog items selected for the Sprint, and the plan for delivering them.
Scrum team members and Sprint Planning
- Product Owner should ensure that the most important Backlog items are known enough for a discussion to start.
- Developers need to be aware of what is likely to go into the sprint and have thought about how the individual items could be implemented.
- The Scrum master should be ready to help with the way Sprint planning is managed or to facilitate it if requested.
- People outside the Scrum team can also participate if the Scrum Team needs their advice.
3 Sprint planning topics
- Why is this Sprint valuable?
- The product owner presents what should be done in a sprint to bring the greatest value. Based on that the Scrum team must create a Sprint goal during planning.
- What can be done this sprint?
- Items from the Product Backlog are selected. It must correspond to the Scrum team capacity which is based on the performance of the previous sprints.
- How will the chosen work get done?
- How to implement the individual items that were selected for the Sprint. Large items can be split for easier implementation. This is developers the responsibility.