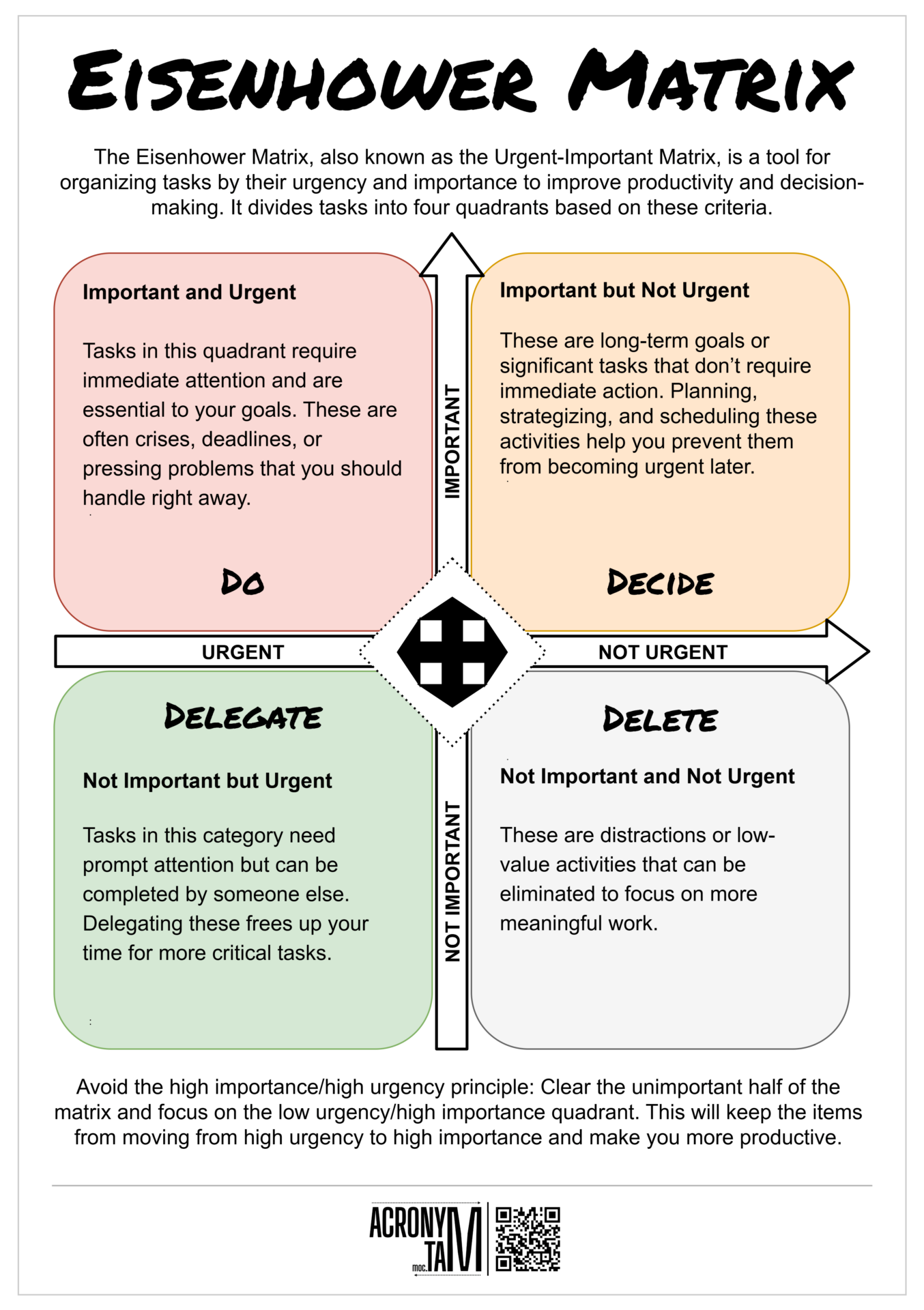
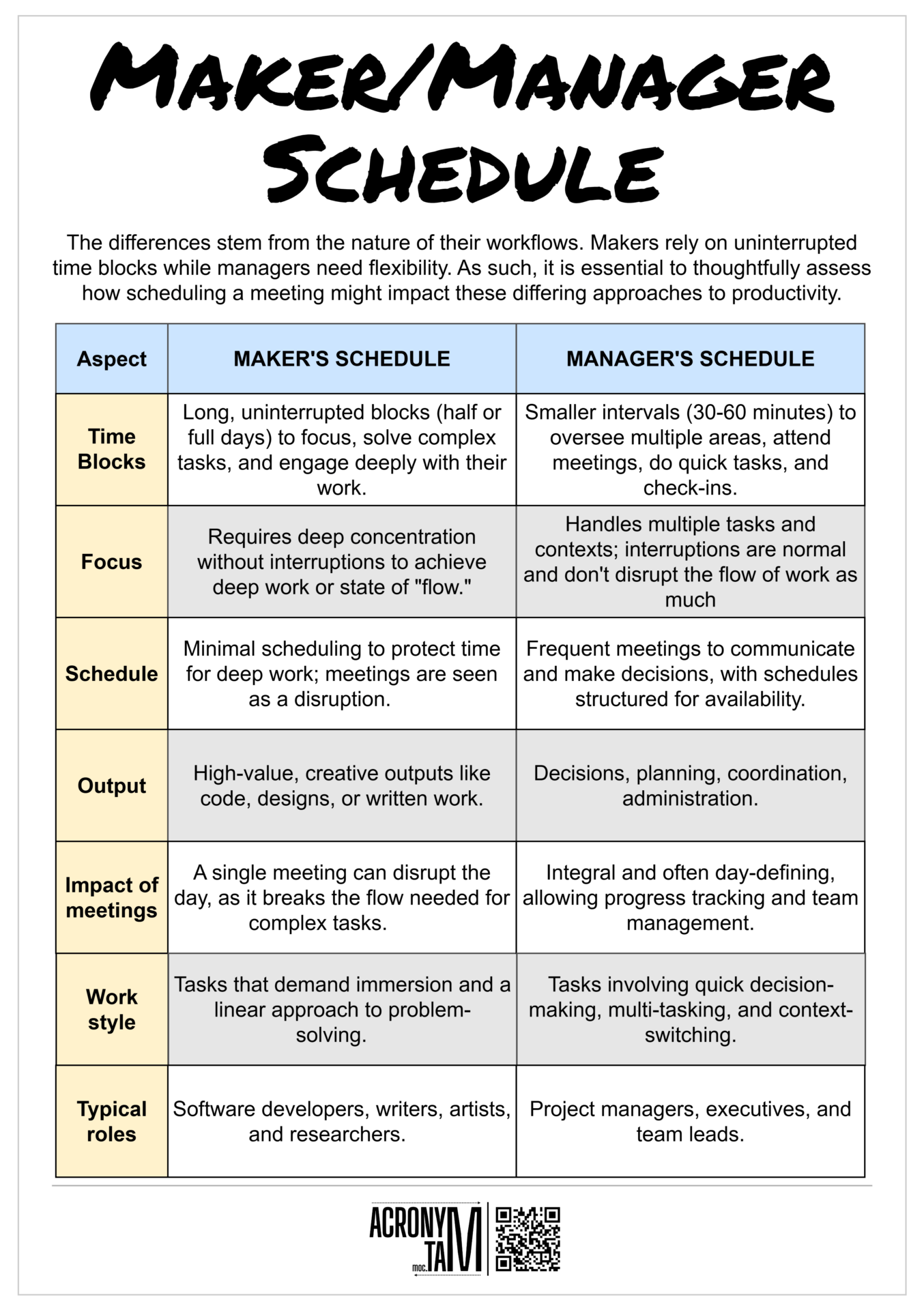
Article
Seven Development Principles
The Reason It All Exists
A software system exists to provide value to its users. This has to be taken into account before every decision, even though the value as a measure is relative.
KISS (Keep It Simple, Stupid!)
All designs should be as simple as possible. Simple designs are usually the most elegant ones (more maintainable and less error-prone).
Maintain the Vision
A clear vision is essential to the success of a software project. The lack of conceptual integrity can lead to multiple different abstractions not working together properly.
What You Produce, Others Will Consume
The system will be used by others, so, keep the audience in mind during the development. Try to produce something easy to use, maintain, etc.
Be Open to the Future
Systems that can last longer have more value. Systems must be ready to adapt to changing requirements. Address this by solving general problems instead of specific ones.
Plan Ahead for Reuse
Reuse saves time and effort. If you can achieve it communicate the reuse opportunities to your peers. They cannot use something they do not know exists.