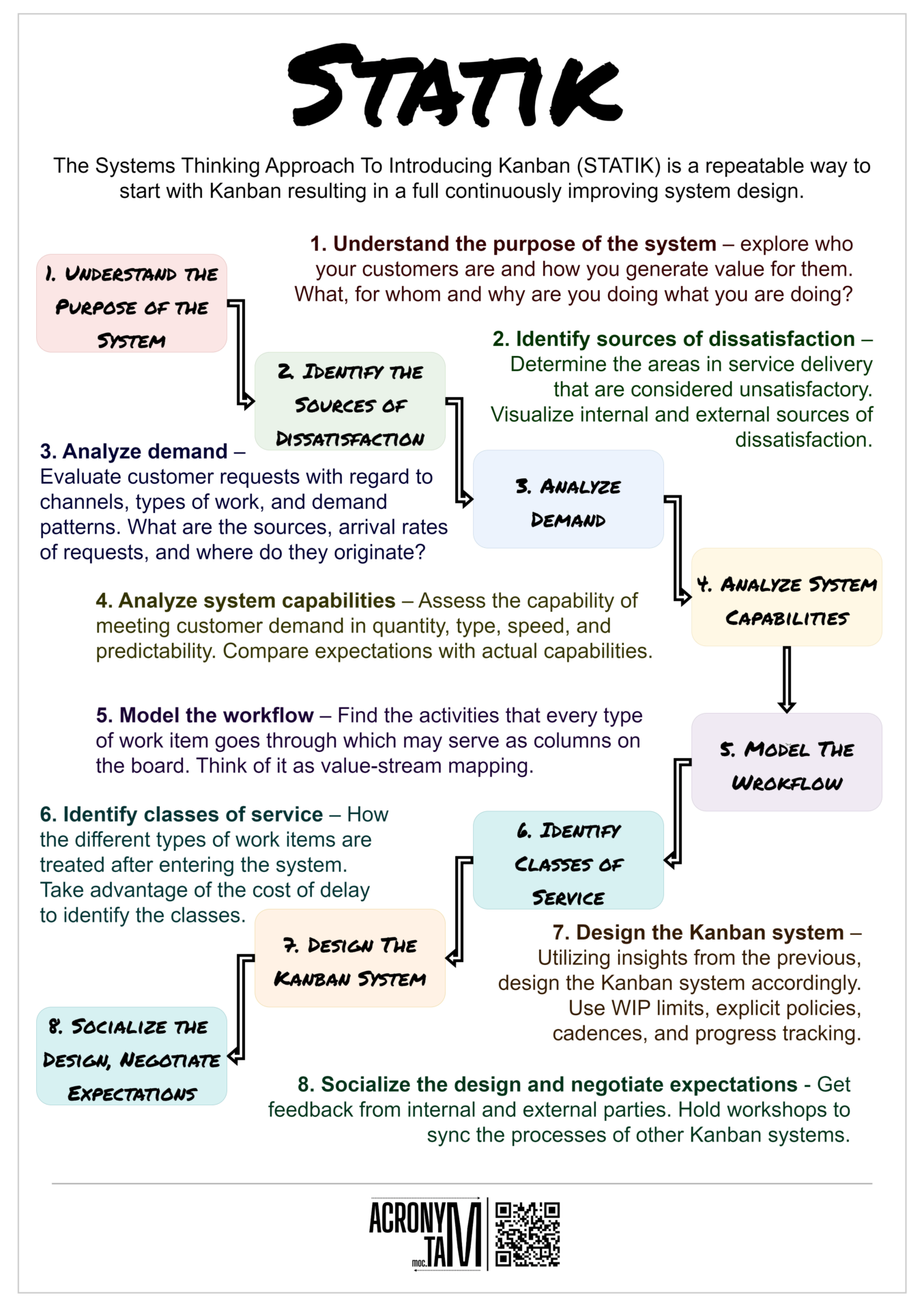
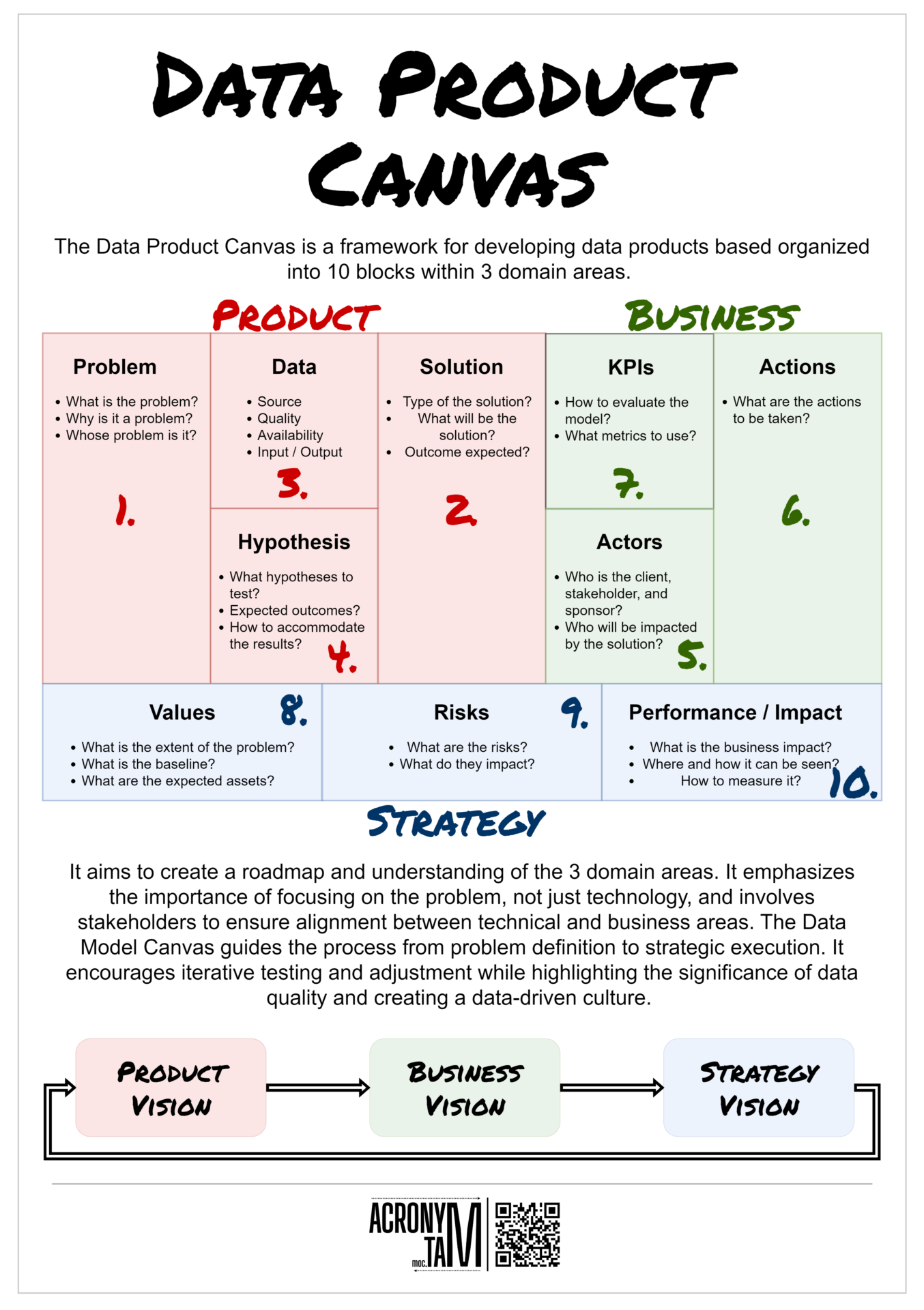
Article
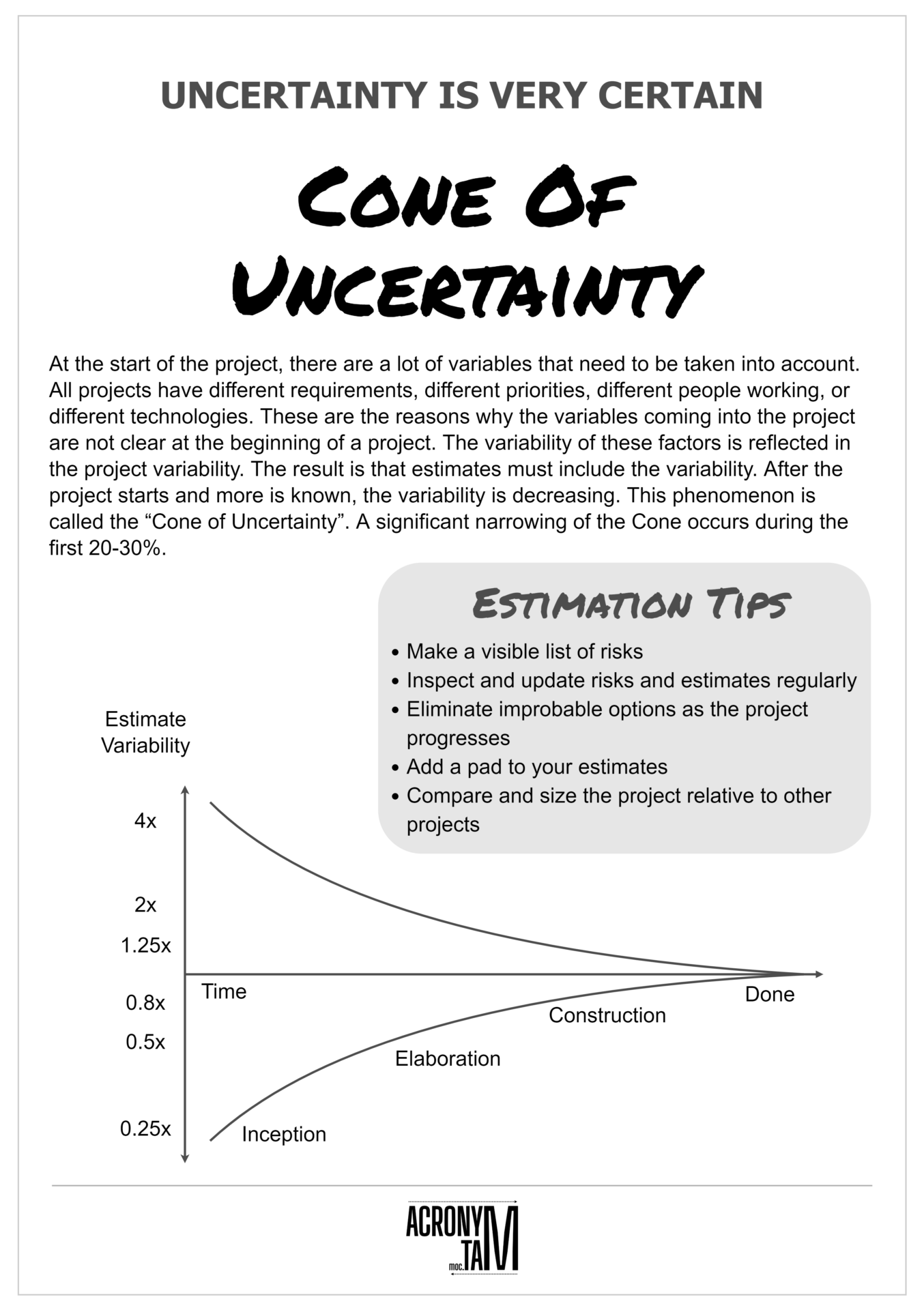
Cone of Uncertainty
Uncertainty is very certain.
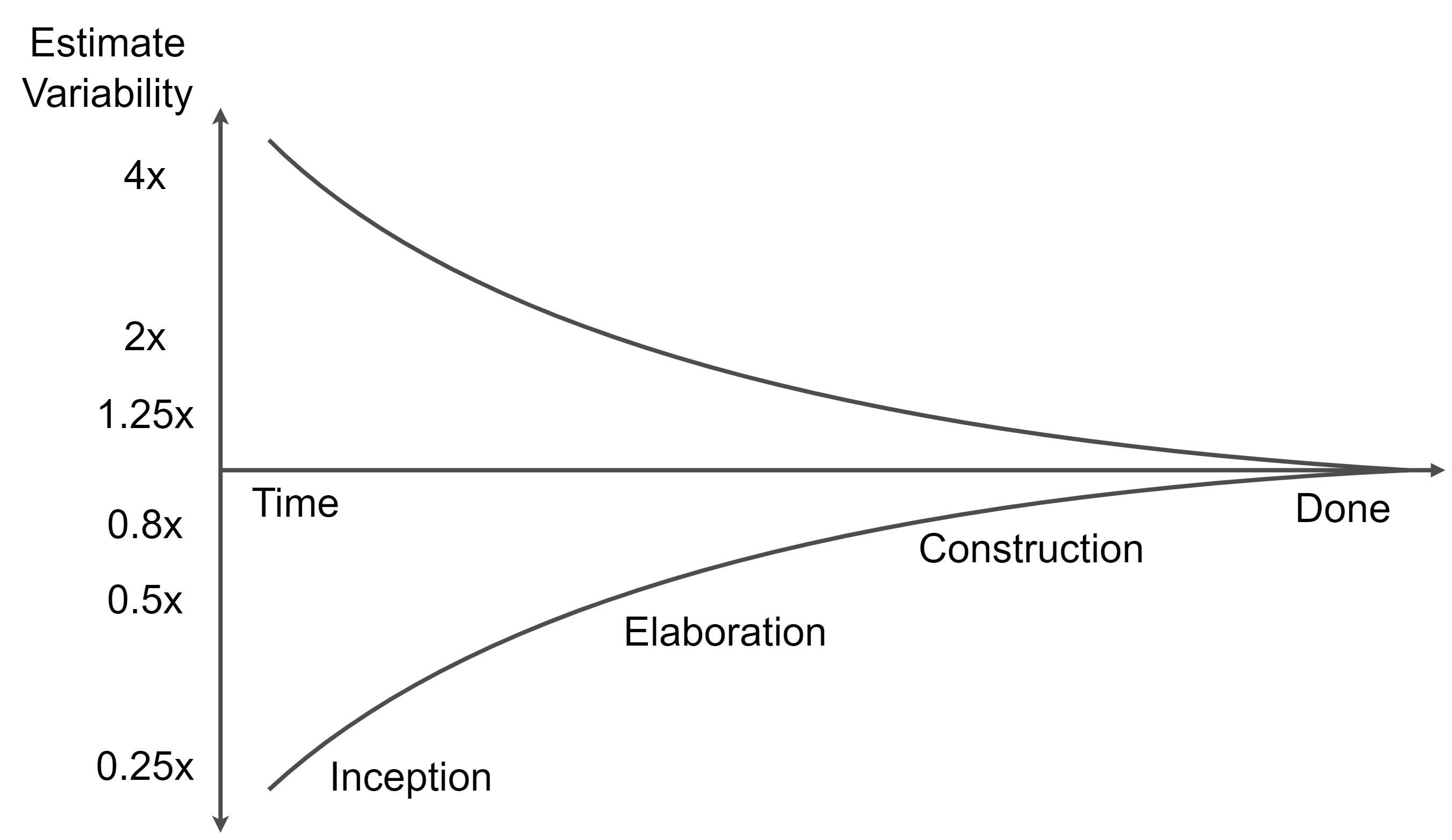
At the start of the project, there are a lot of variables that need to be taken into account. All projects have different requirements, different priorities, different people working, or different technologies. These are the reasons why the variables coming into the project are not clear at the beginning of a project. The variability of these factors is reflected in the project variability. The result is that estimates must include the variability. After the project starts and more is known, the variability is decreasing. This phenomenon is called the “Cone of Uncertainty”. A significant narrowing of the Cone occurs during the first 20-30%.
Estimation tips
- Make a visible list of risks
- Inspect and update risks and estimates regularly
- Eliminate improbable options as the project progresses
- Add a pad to your estimates
- Compare and size the project relative to other projects