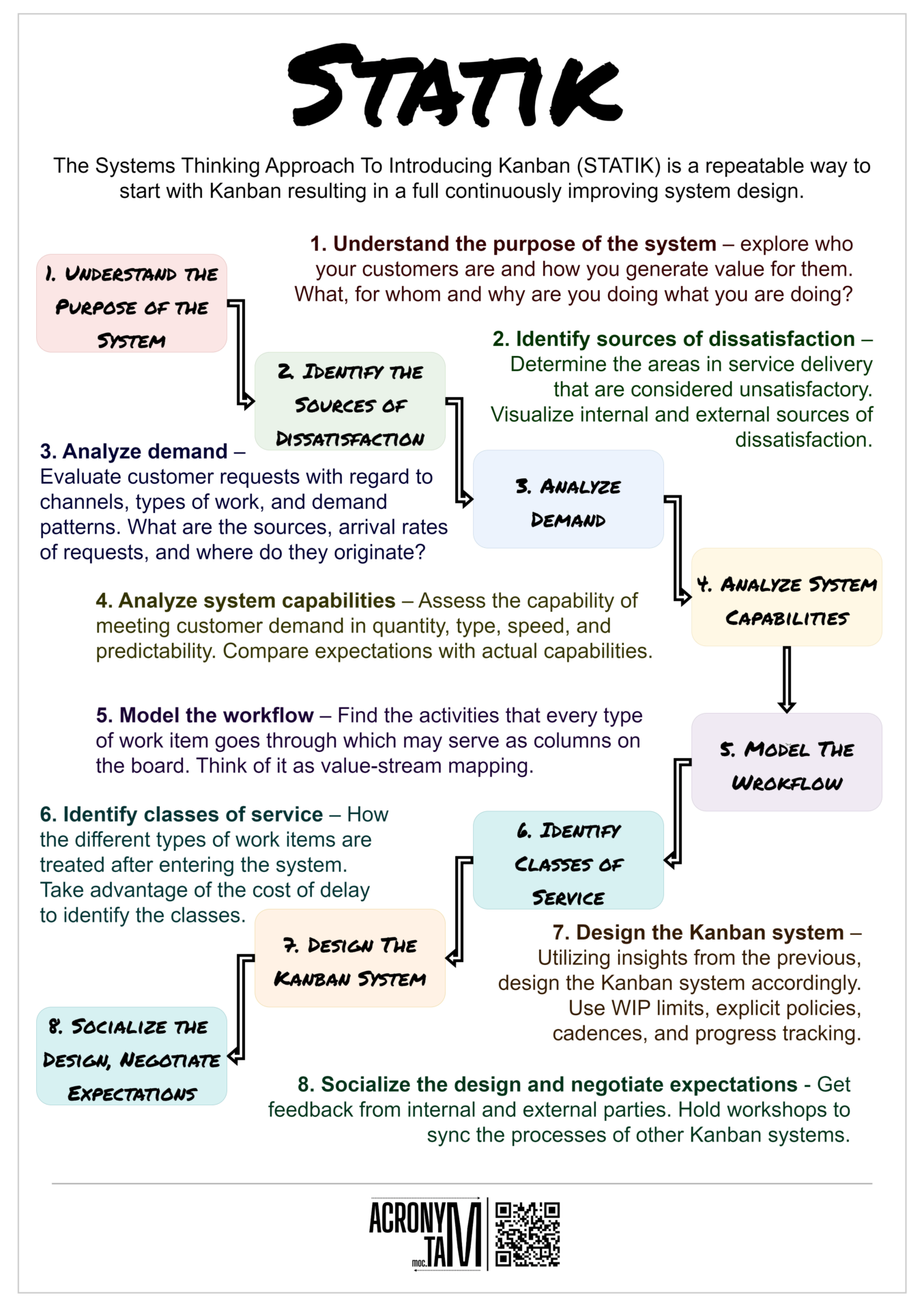
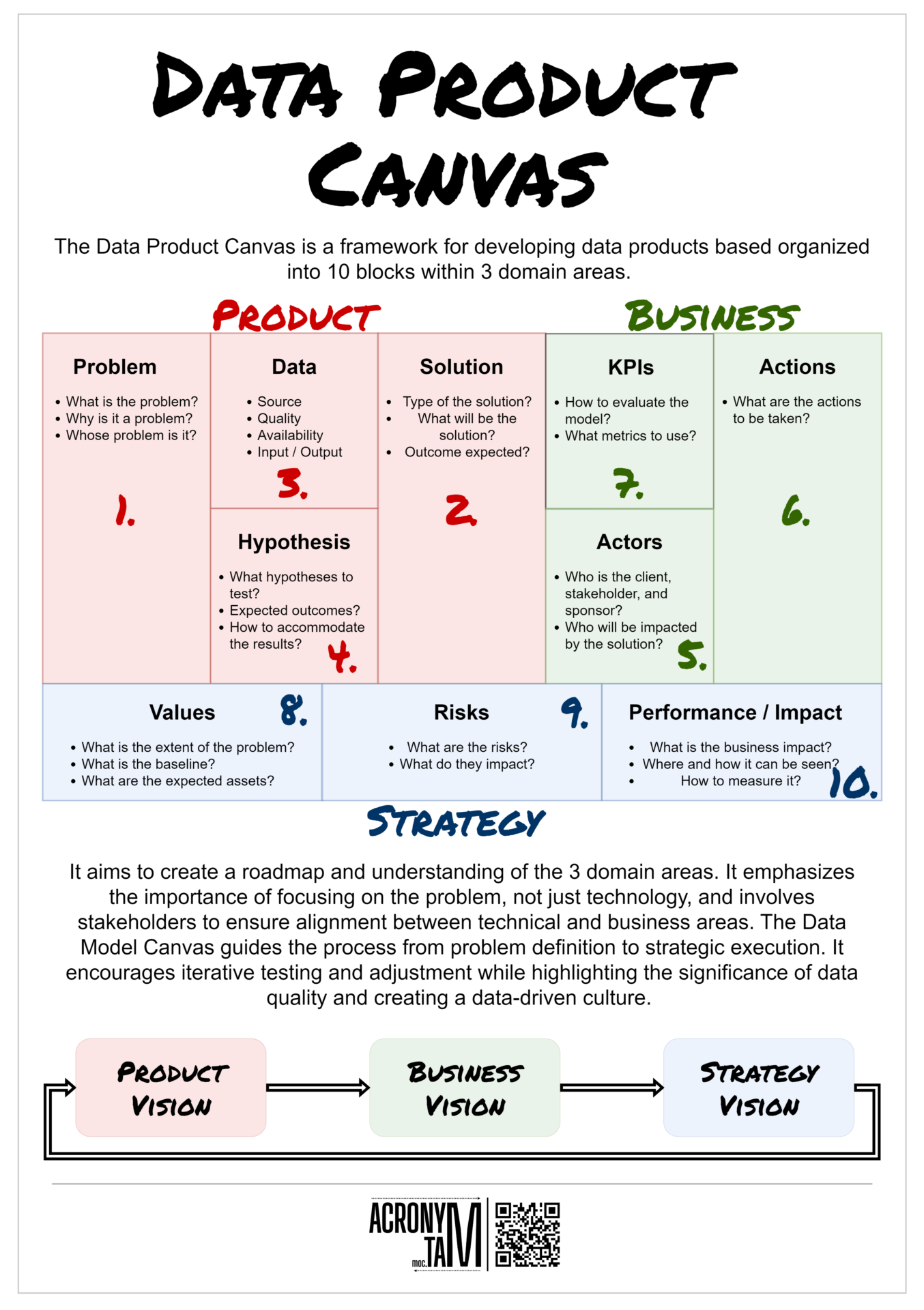
Article
PDCA – Deming Cycle / Stewhart Cycle
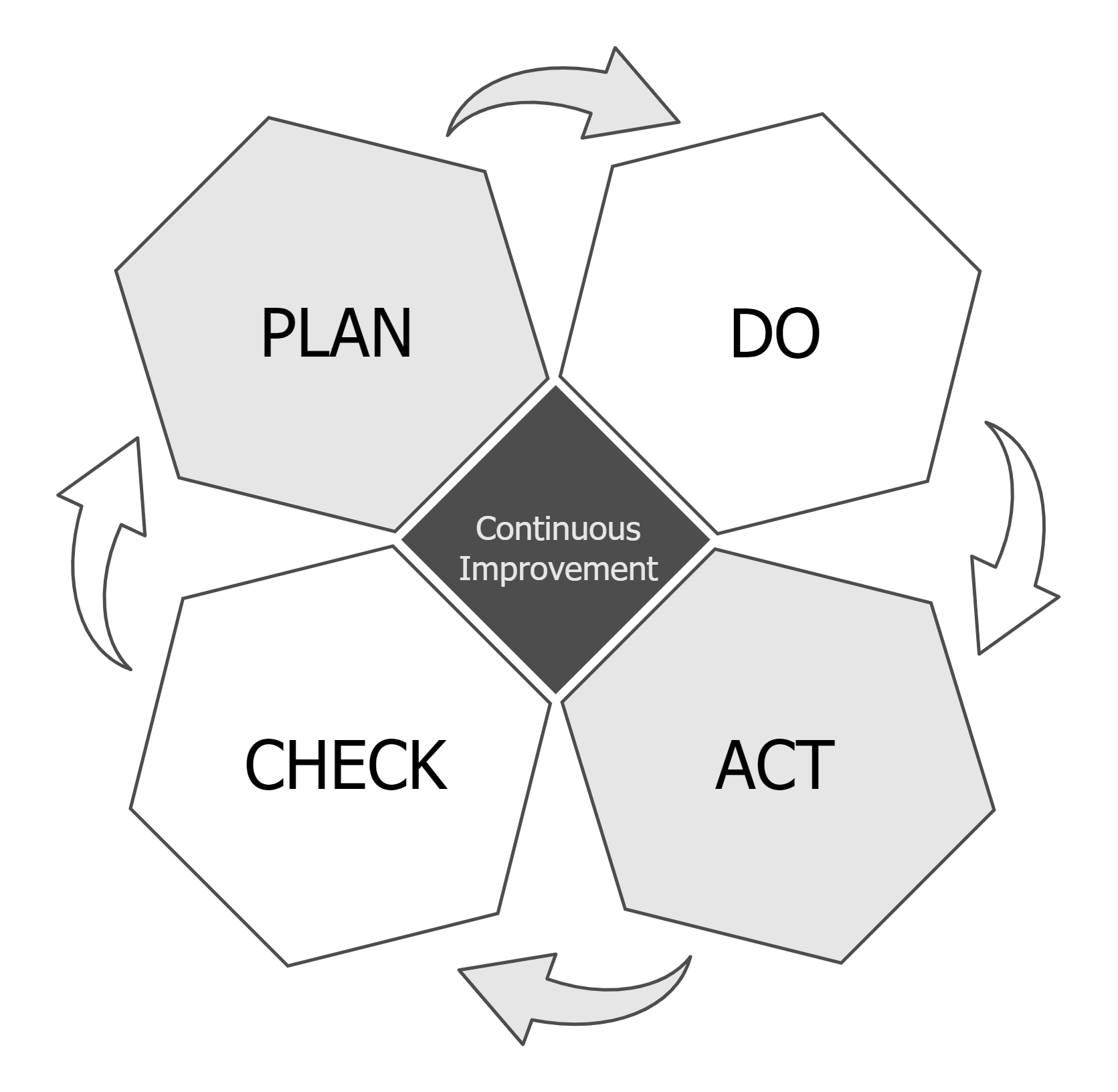
The continuous improvement cycle model, which is a core part of lean manufacturing. It is an iterative process helping to avoid recurring mistakes, extending knowledge by repeating its stages.
Plan
Create a plan for the iteration. Identify and understand your problem or opportunity and create a plan for satisfying the goals set. Usually, small steps are used for eliminating failures.
Do
The plan from the previous stage is executed. While executing the plan problems may occur and should be recorded. Execution data should be gathered for further analysis.
Check
Analyze what was done in the previous stages and compare the outcomes against the goals. If there were problems the root cause of the problems needs to be identified.
Act
Based on the outcomes of the Check phase an action to standardize or improve the process is taken if needed. Since the PDCA is a loop you go back to the first stage and use the outcomes of the first loop as a base for the next iteration.