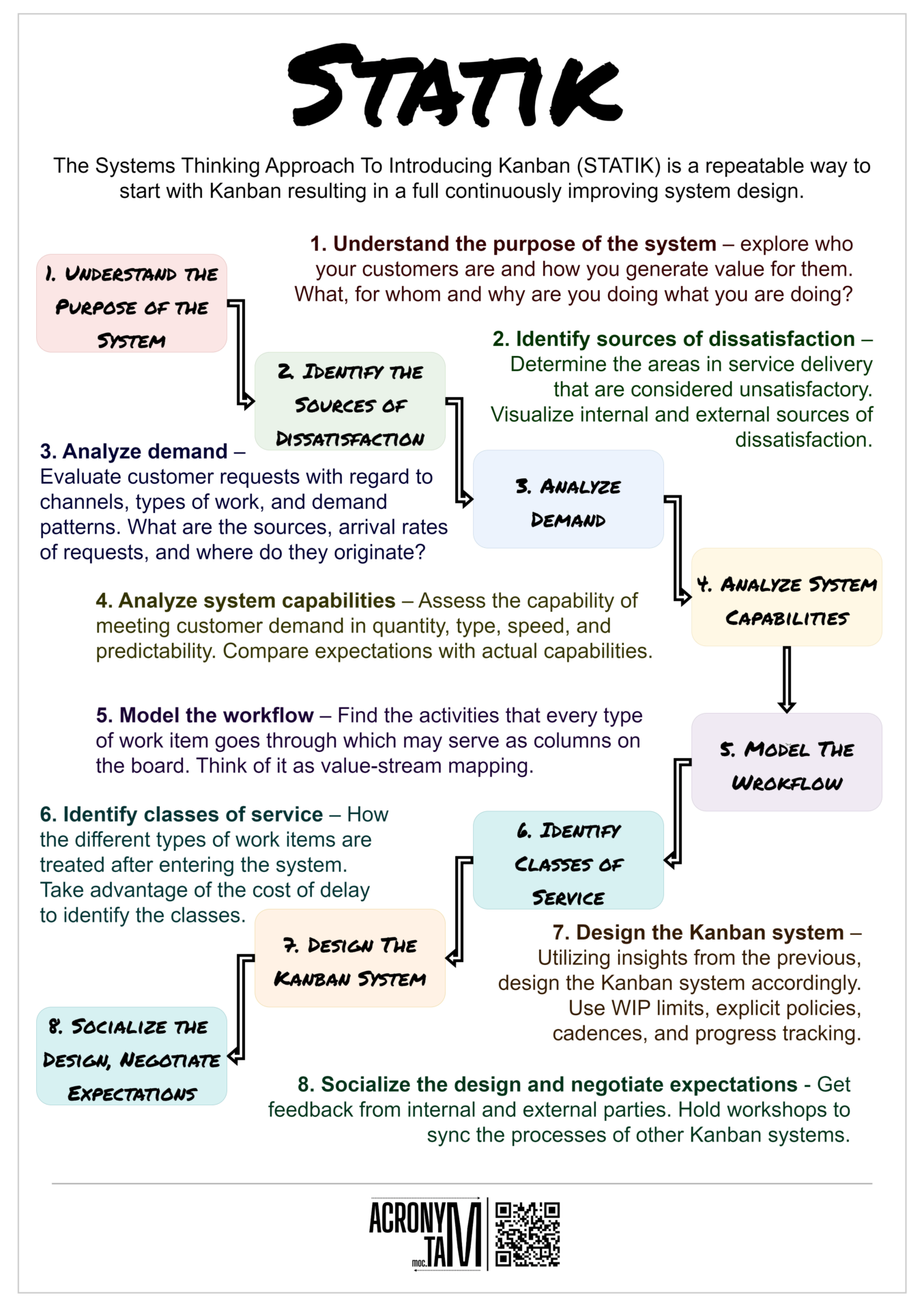
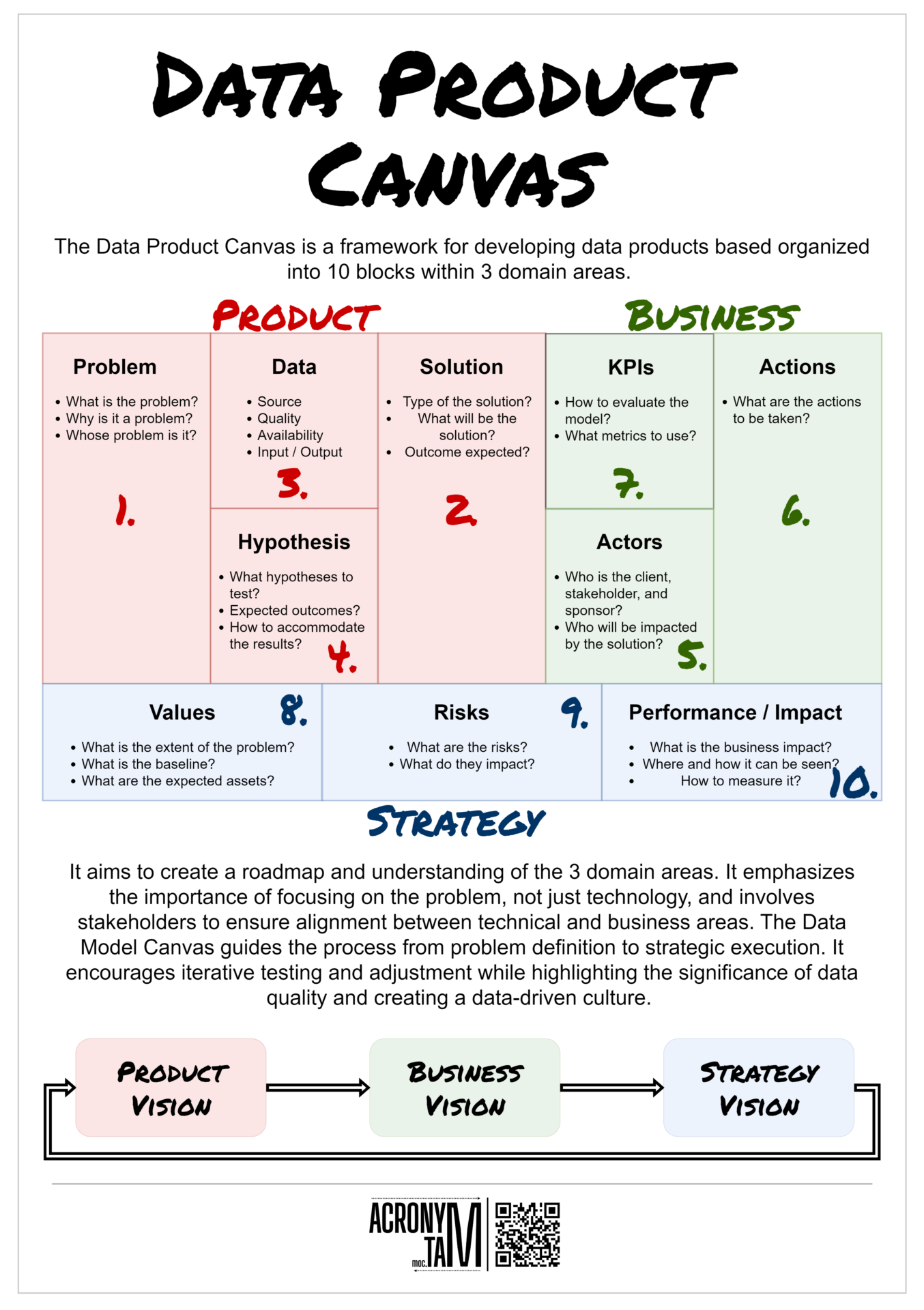
Article
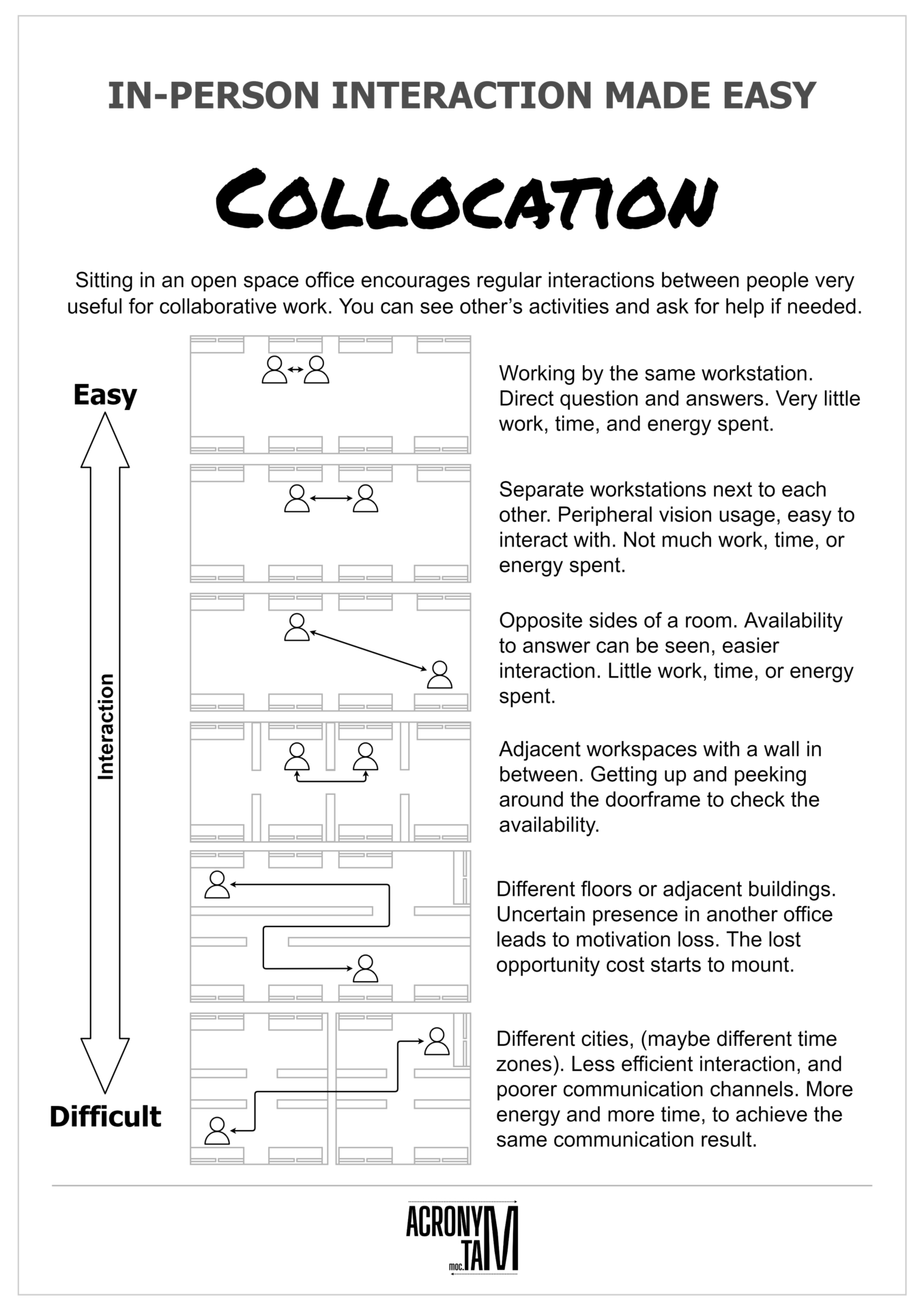
Collocation
Collocation – Sitting in an open space office encourages regular interactions between people very useful for collaborative works. You can see other’s activities and ask for help if needed.
Working by the same workstation. Direct question and answers. Very little work, time, and energy spent.
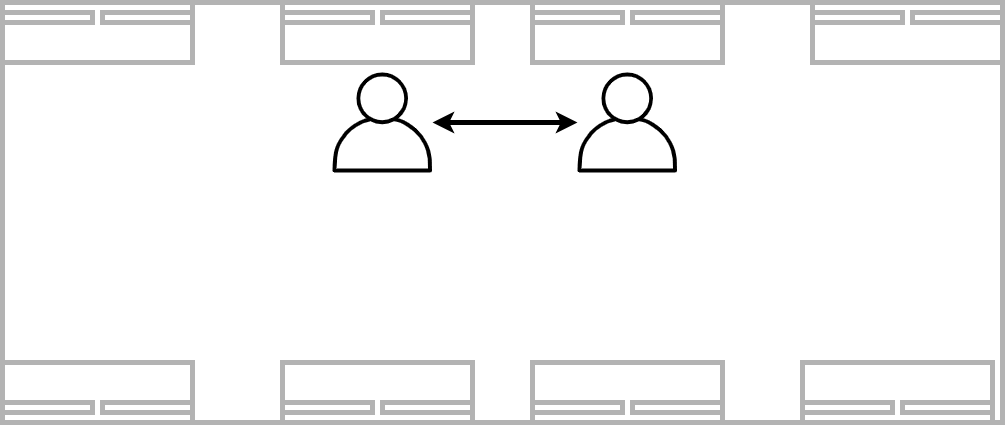
Separate workstations next to each other. Peripheral vision usage, easy to interact. Not much work, time, or energy spent.
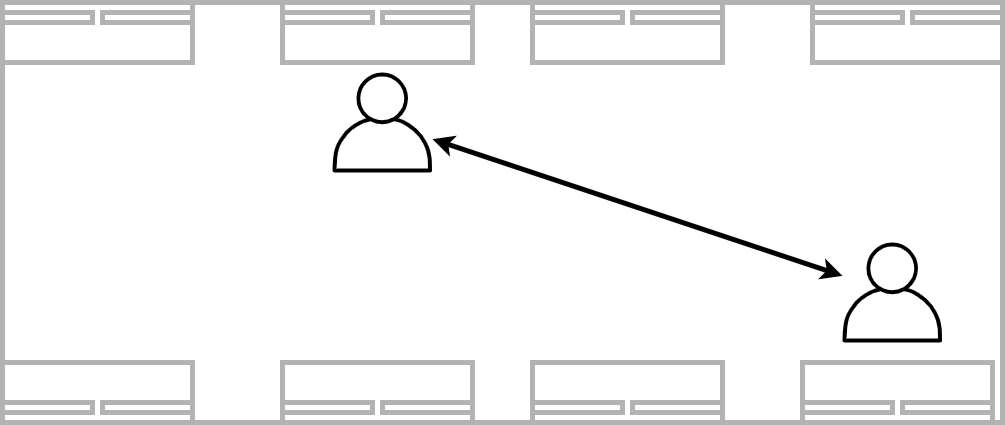
Opposite sides of a room. Availability to answer can be seen, easier interaction. Little work, time, or energy spent.
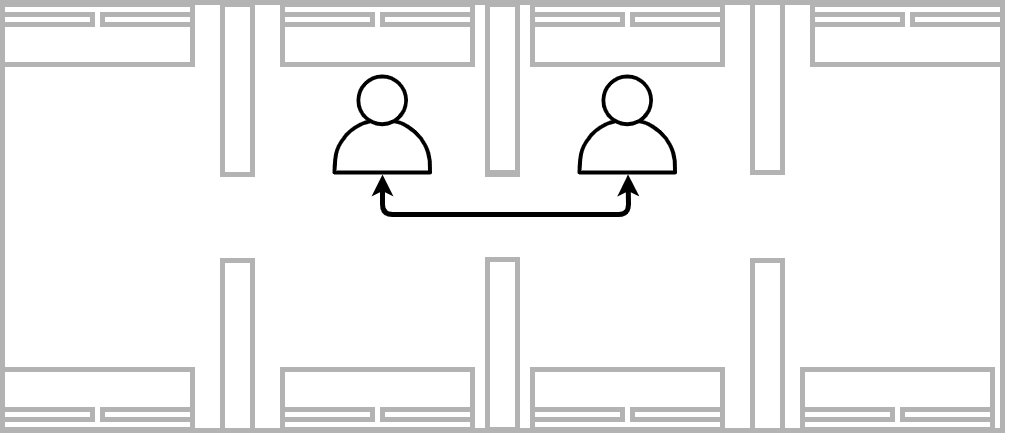
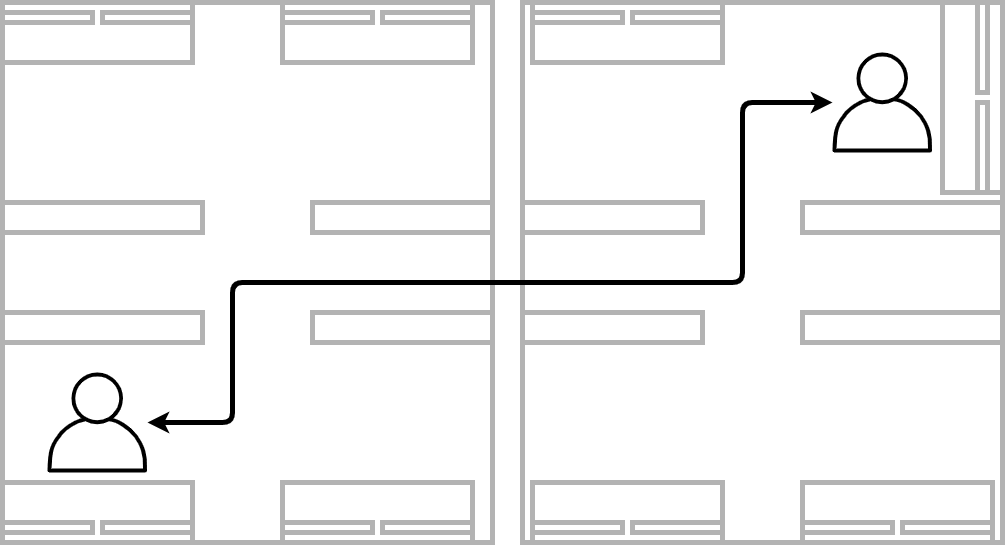
Adjacent workspaces with a wall in between. Getting up and peeking around the doorframe to check the availability.
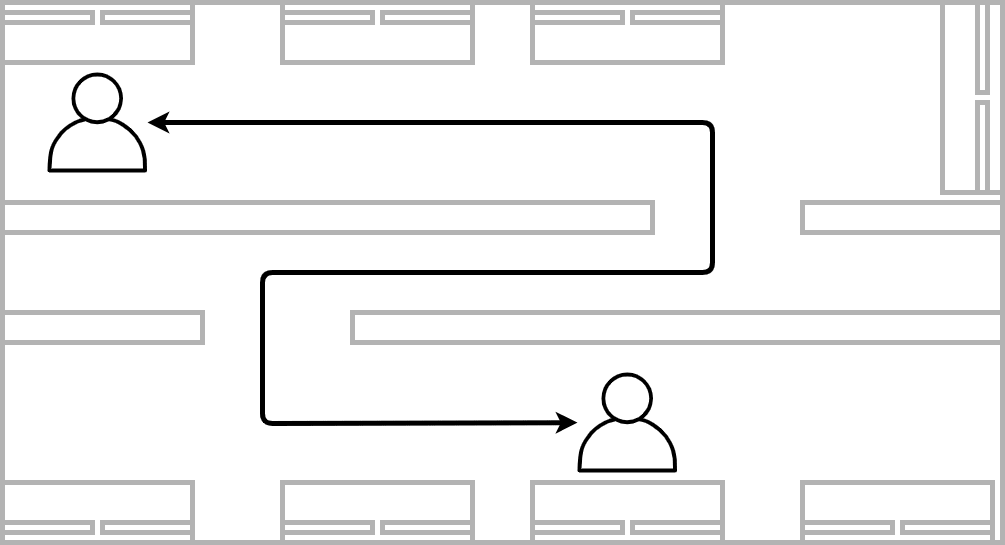
Different floors or adjacent buildings. The need of going to another office with an uncertain presence can lead to the loss of motivation. The lost opportunity cost starts to mount.
Different cities, (maybe different time zones). Less efficient interaction, poorer communication channels. More energy and more time, to achieve the same communication result.