Article
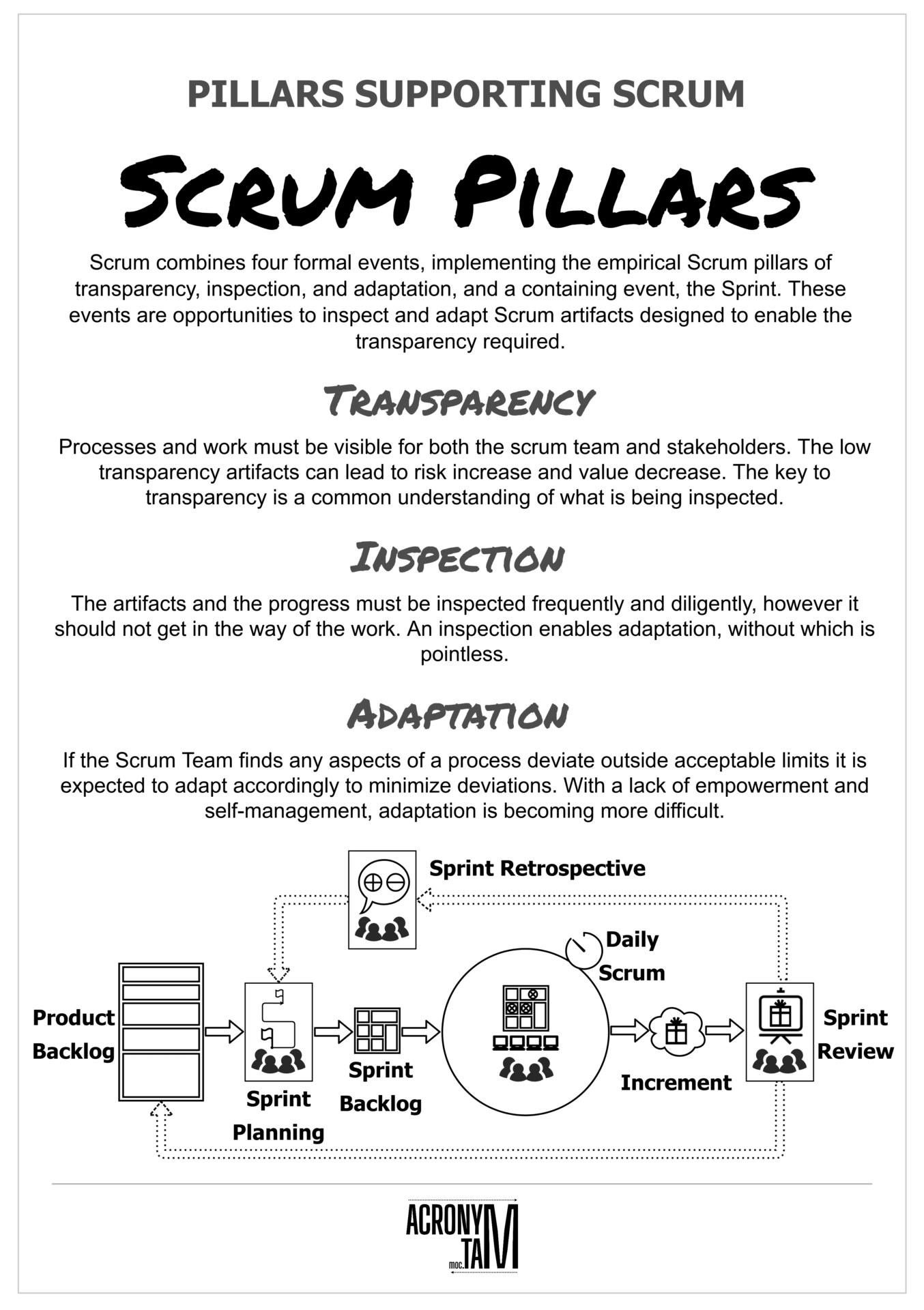
Scrum Pillars
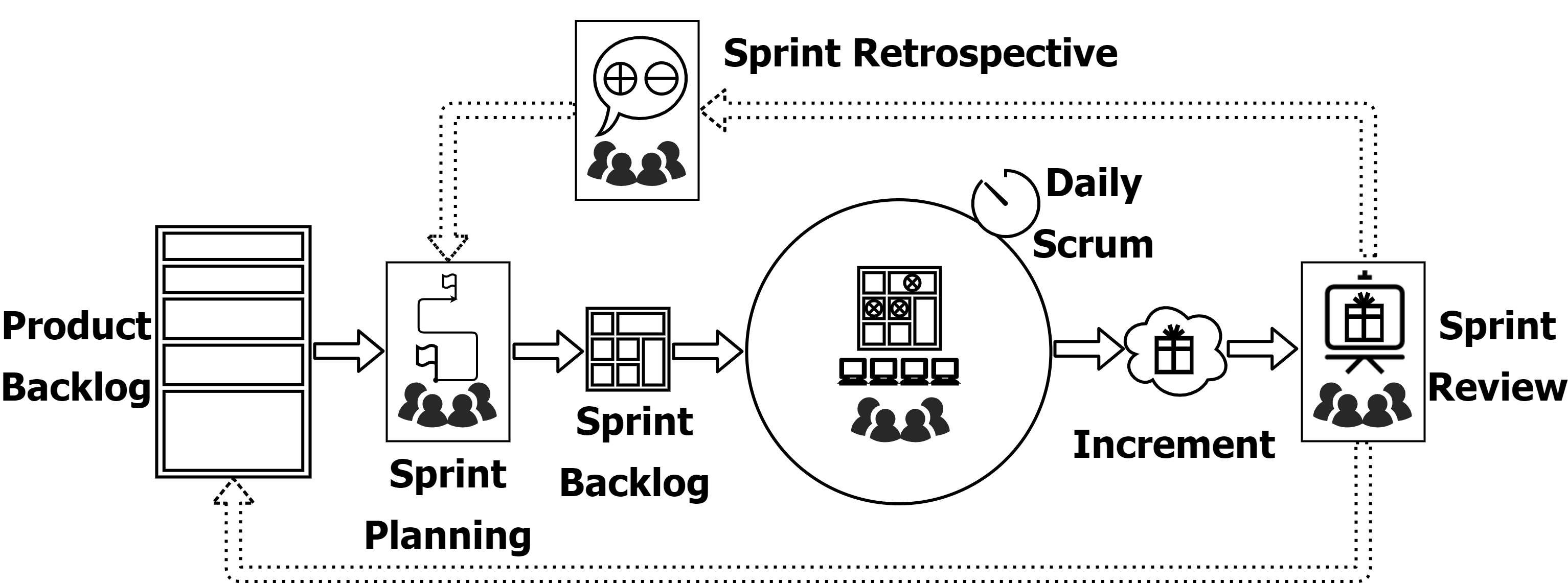
Scrum combines four formal events, implementing the empirical Scrum pillars of transparency, inspection, and adaptation, and a containing event, the Sprint. These events are opportunities to inspect and adapt Scrum artifacts designed to enable the transparency required.
Transparency
Processes and work must be visible for both the scrum team and stakeholders. The low transparency artifacts can lead to risk increase and value decrease. The key to transparency is a common understanding of what is being inspected.
Inspection
The artifacts and the progress must be inspected frequently and diligently, however it should not get in the way of the work. An inspection enables adaptation, without which is pointless.
Adaptation
If the Scrum Team finds any aspects of a process deviate outside acceptable limits it is expected to adapt accordingly to minimize deviations. With a lack of empowerment and self-management, adaptation is becoming more difficult.