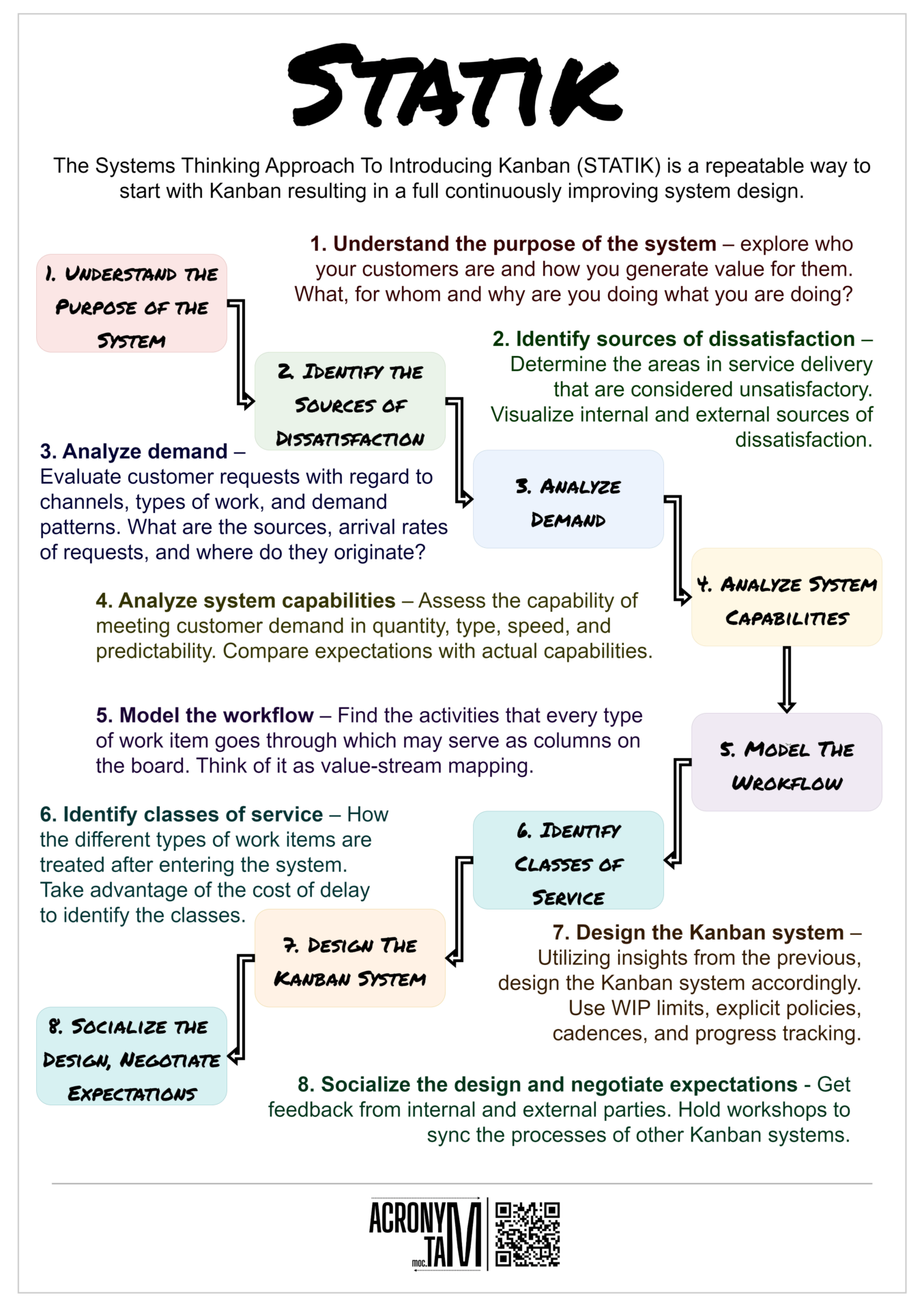
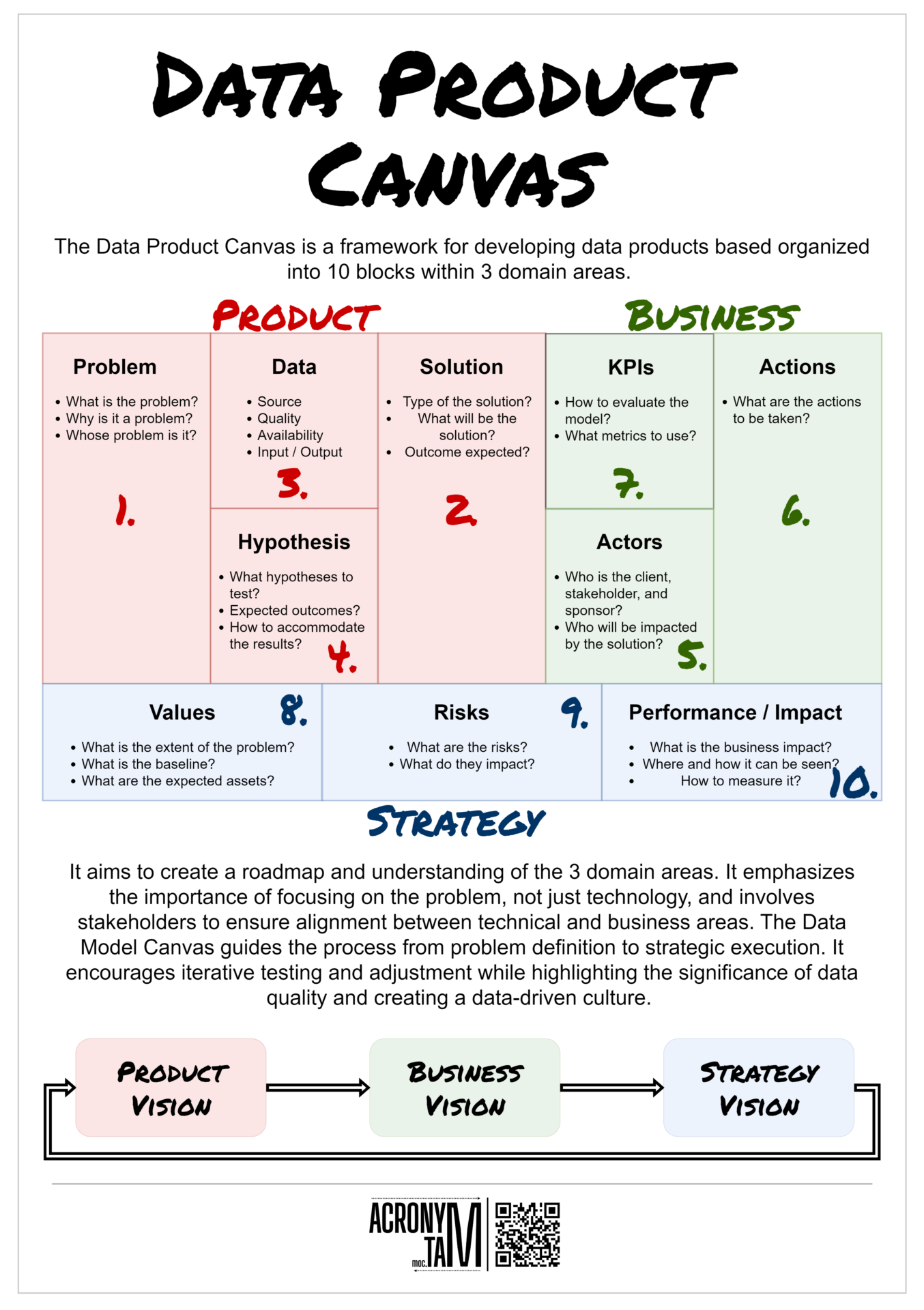
Article
Evidence Based Management
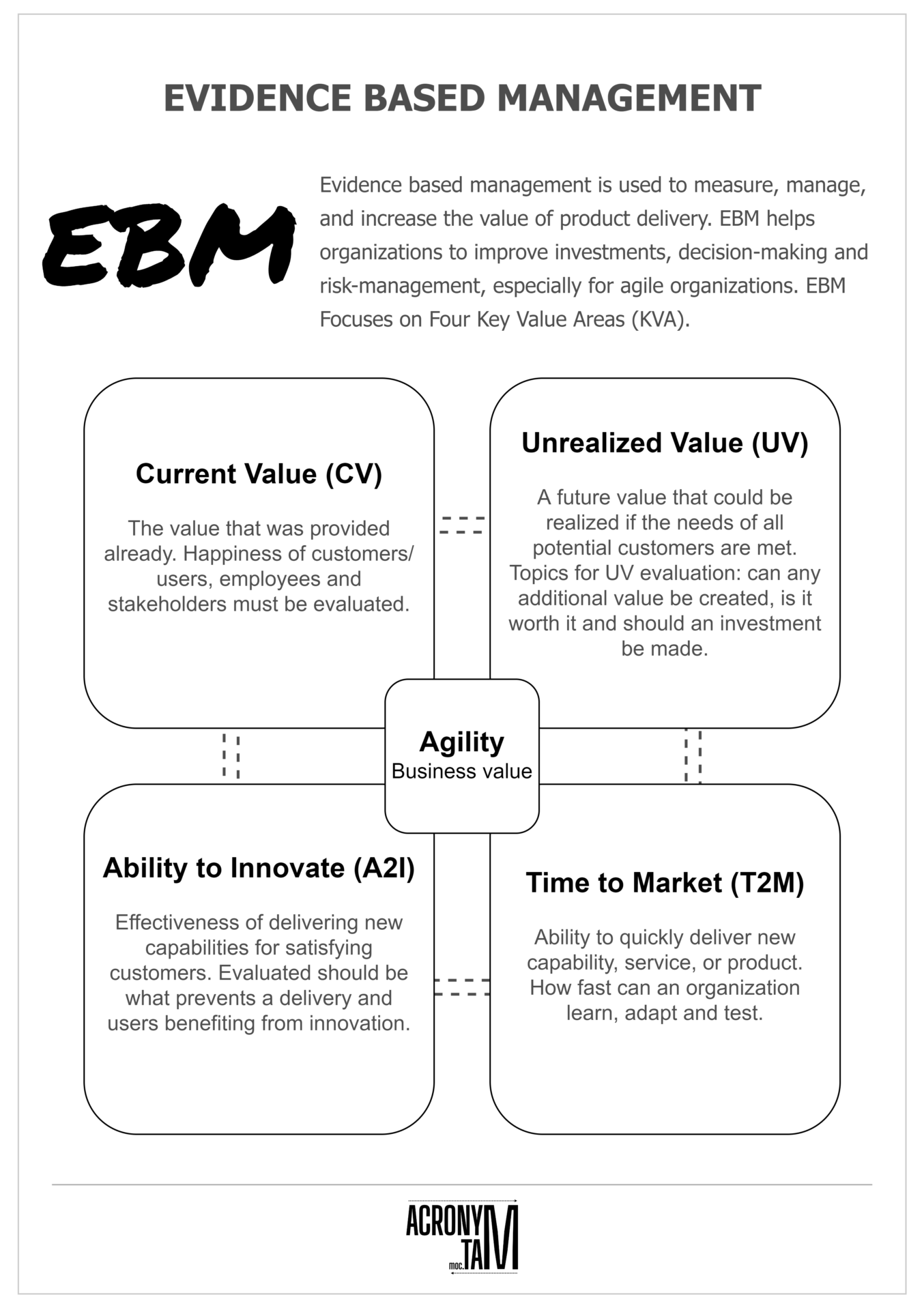
Evidence based management is used to measure, manage, and increase the value of product delivery. EBM helps organizations to improve investments, decision-making and risk-management, especially for agile organizations. EBM Focuses on Four Key Value Areas.
Four Key Value Areas (KVA)
Unrealized Value (UV)
A future value that could be realized if the needs of all potential customers are met. Topics for UV evaluation: can any additional value be created, is it worth it and should an investment be made.
Current Value (CV)
The value that was provided already. Happiness of customers / users, employees and stakeholders must be evaluated.
Ability to Innovate (A2I)
Effectiveness of delivering new capabilities for satisfying customers. Evaluated should be what prevents a delivery and users benefiting from innovation.
Time to Market (T2M)
Ability to quickly deliver new capability, service, or product. How fast can an organization learn, adapt and test.
- scrum.org
- The Evidence-Based Management Guide
- wikipedia.org