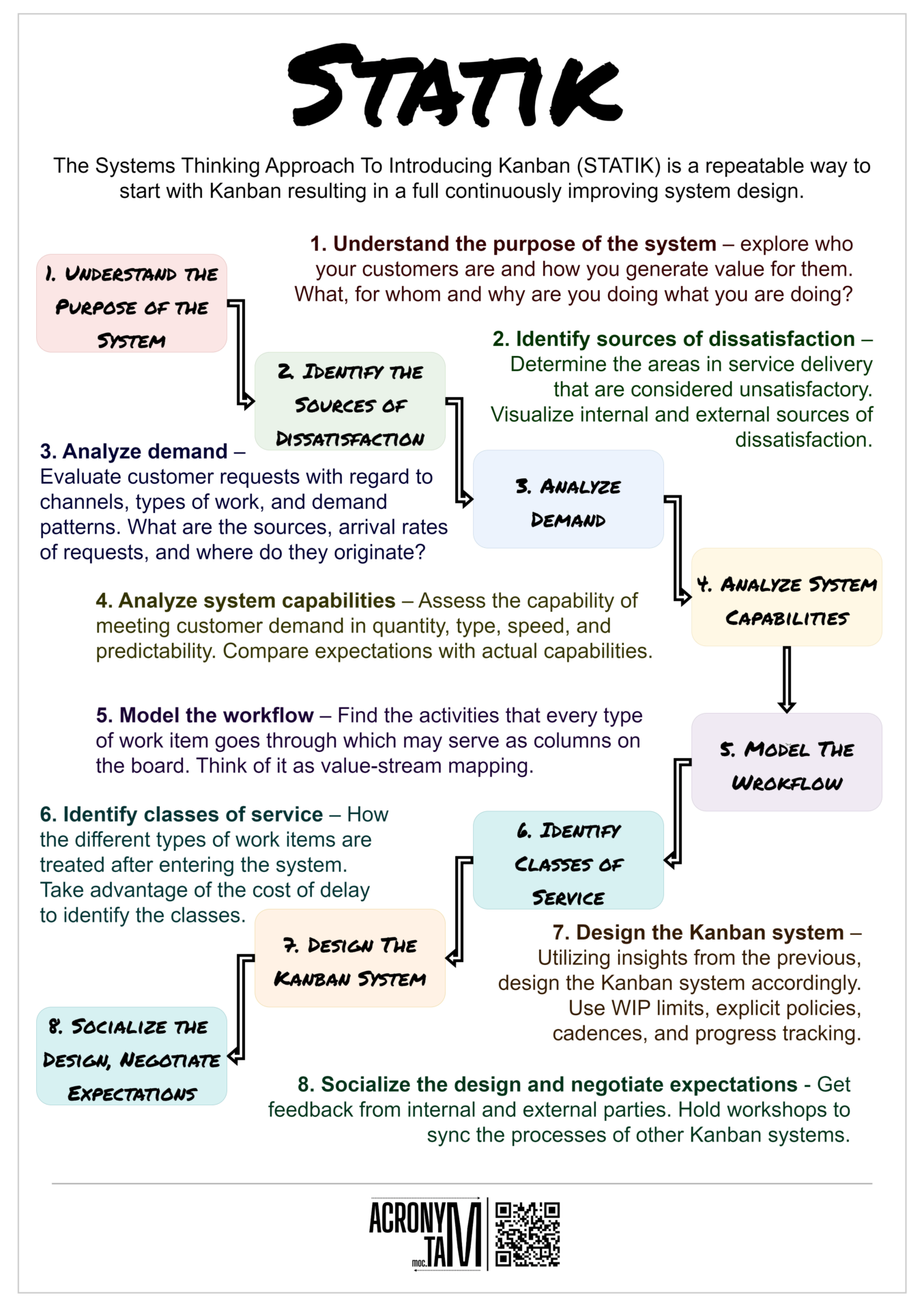
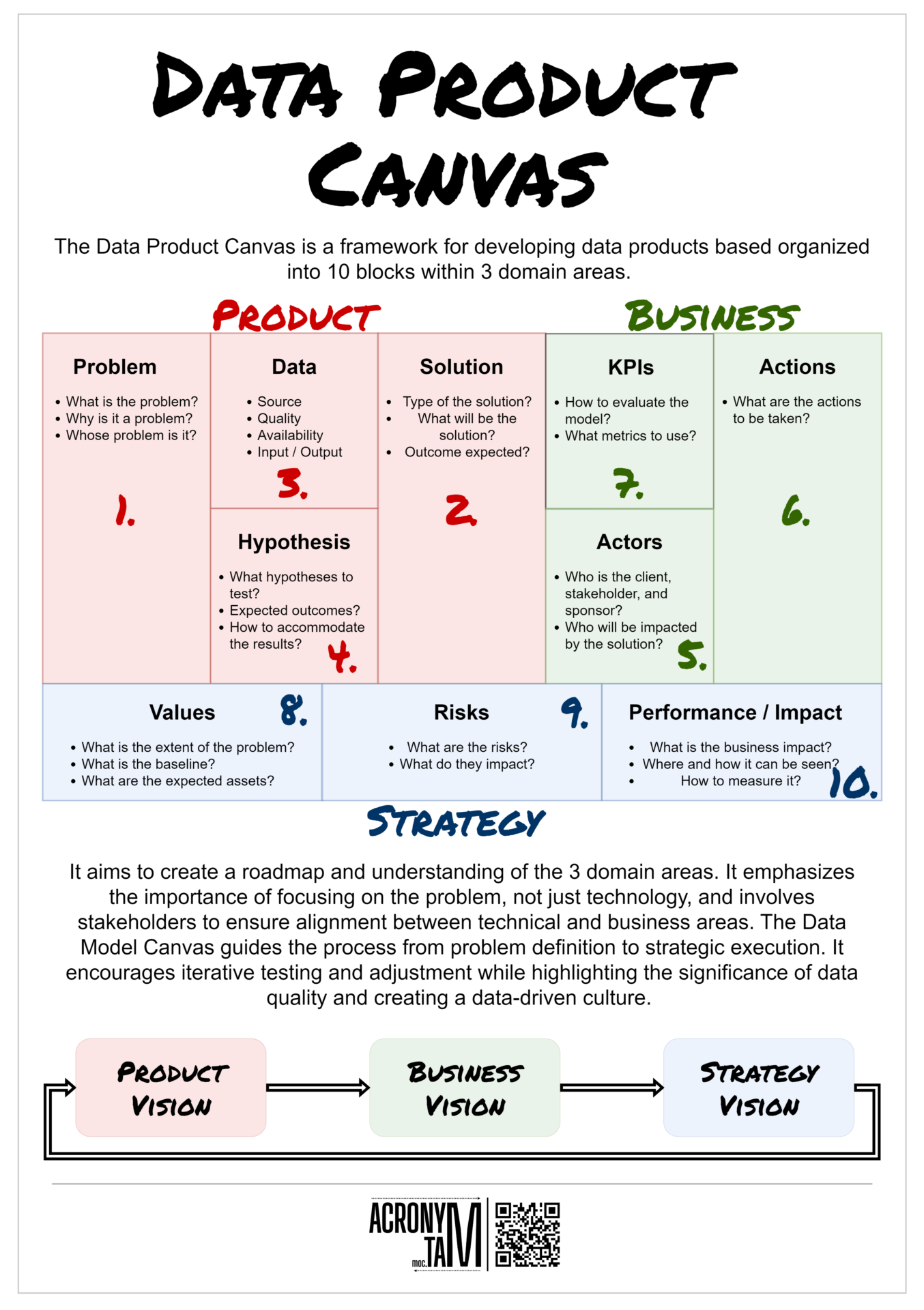
Article
Definition of Ready
Serves as a precondition for an item from Product Backlog before entering a Sprint/ Iteration backlog to prevent problems before it starts. It is important to find the balance while specifying the DoR as it has to provide enough space for a team to work in an agile way. If you are using this practice then in the prioritized backlog the items on the top should meet the DoR criteria. The state of meeting defined DoR criteria can be ranked, for example with medals (bronze, silver, gold).
Examples of good DoR criteria
- Item is estimated
- Item can be finished within one iteration
- Acceptance criteria has been provided
- Item follows the INVEST principle
Examples of invalid DoR criteria
- Mock screens for all the views are provided
- The technical solution is provided
- Item is assigned to somebody
Concrete DoR example for User Story
- Clear and appropriate name/ summary label
- The Description in the User Story format is provided as following: As a “user” with “role”, I want “goal” so that “benefit”
- Acceptance criteria/ conditions of satisfaction are provided
- Estimated with measures like:
- Story Points value based on Fibonacci sequence (Preferred)
- T-shirt sizes (XS, S, M, L, XL)
- Dog breeds sizes (Chihuahua – Great Dane)
- User Story follow INVEST acronym: INVEST: Independent Negotiable Valuable Estimable Small Testable
- Sub-tasks follow SMART acronym: SMART: Specific Measurable Accepted Reasonable Time Bound
- Additional information like mock screens, flow diagrams, etc. (Optional)