Article
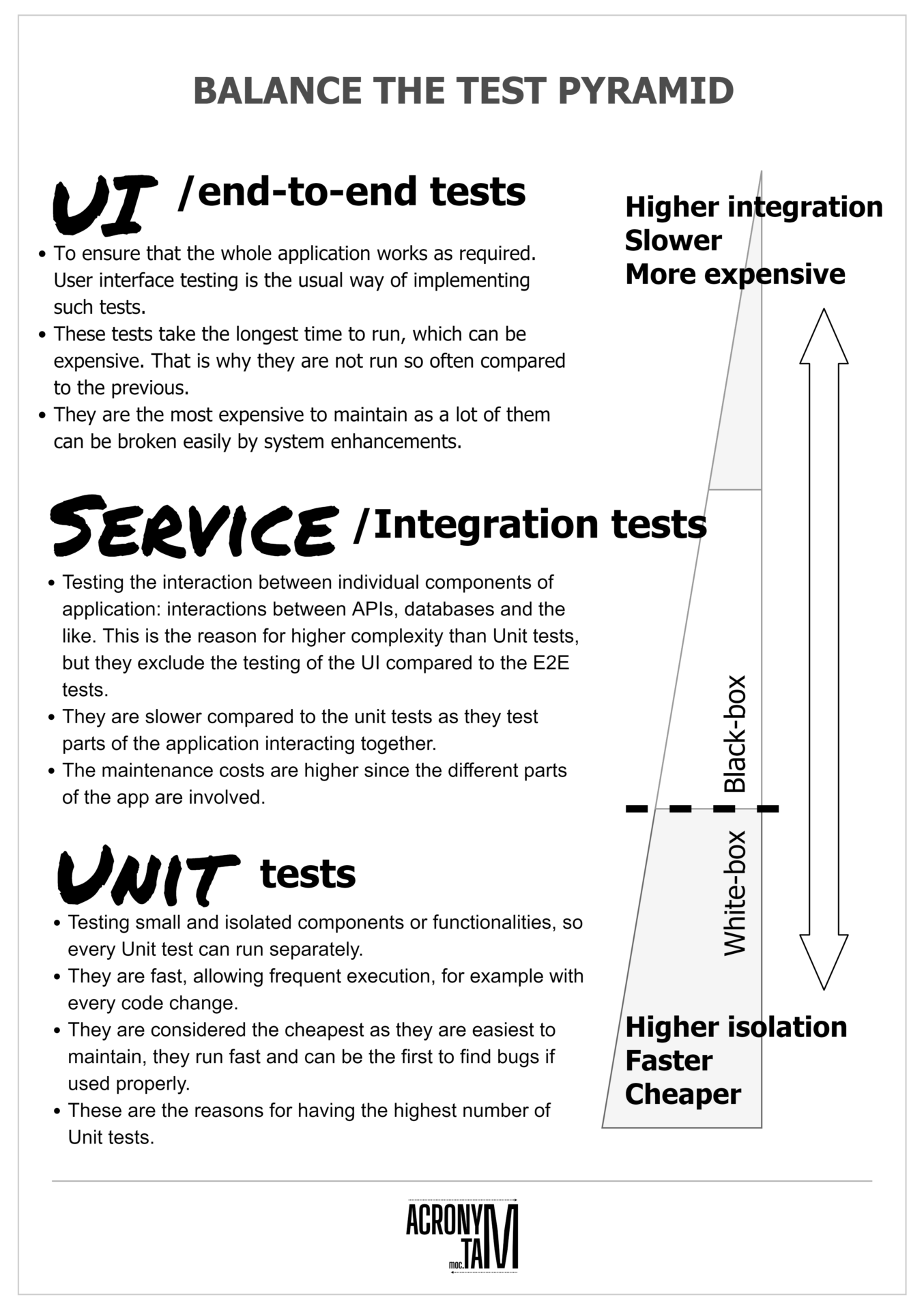
Testing Pyramid
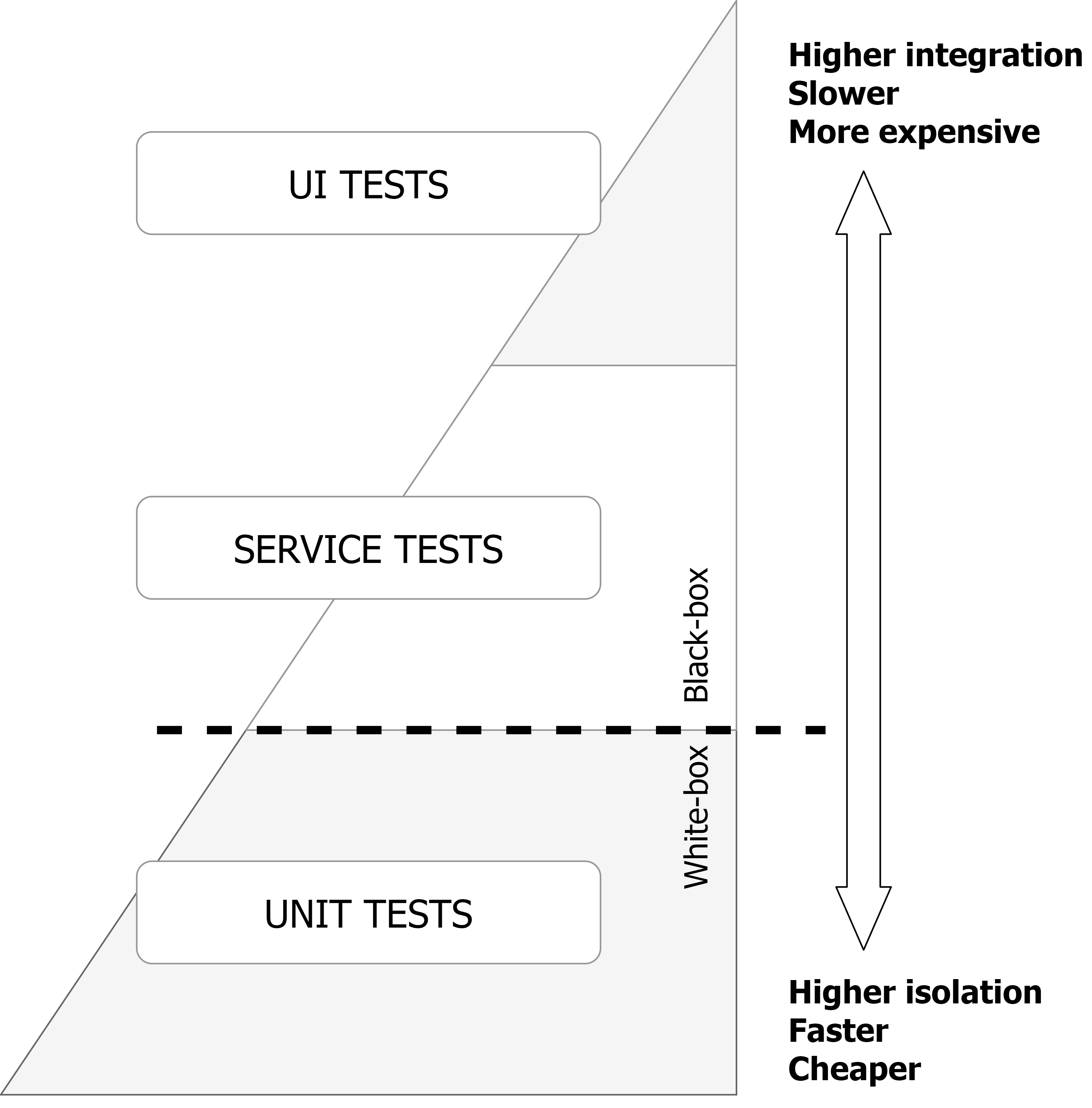
Unit tests
- Testing individual components or functionalities. They are small and isolated, so every Unit test can run separately.
- They are fast, so they can be executed often. The good practice is to execute the Unit tests with every code change.
- They are considered the cheapest as they are easiest to maintain, they run fast and can be the first to find mistakes if used properly.
- These are the reasons for having the highest number of Unit tests.
System / Integration tests
- Testing the interaction between individual components of application as interactions between APIs, databases and the like. This is the reason for higher complexity than Unit tests, but they exclude the testing of the UI compared to the E2E tests.
- They are slower compared to the unit tests as they test parts of the application interacting together.
- The maintenance costs are higher since the different parts of the app are involved.
User Interface (UI) / End-to-end (E2E) tests
- To ensure that the whole application works as required. User interface testing is the usual way of implementing such tests.
- These tests take the longest time to run, which can be expensive. That is why they are not run so often compared to the previous.
- They are the most expensive to maintain as a lot of them can be broken easily by system enhancements.