Article
Scrum framework
- Transparency
- Inspection
- Adaptation
- Commitment
- Focus
- Openness
- Respect
- Courage
- Scrum Master
- Product Owner
- Developers
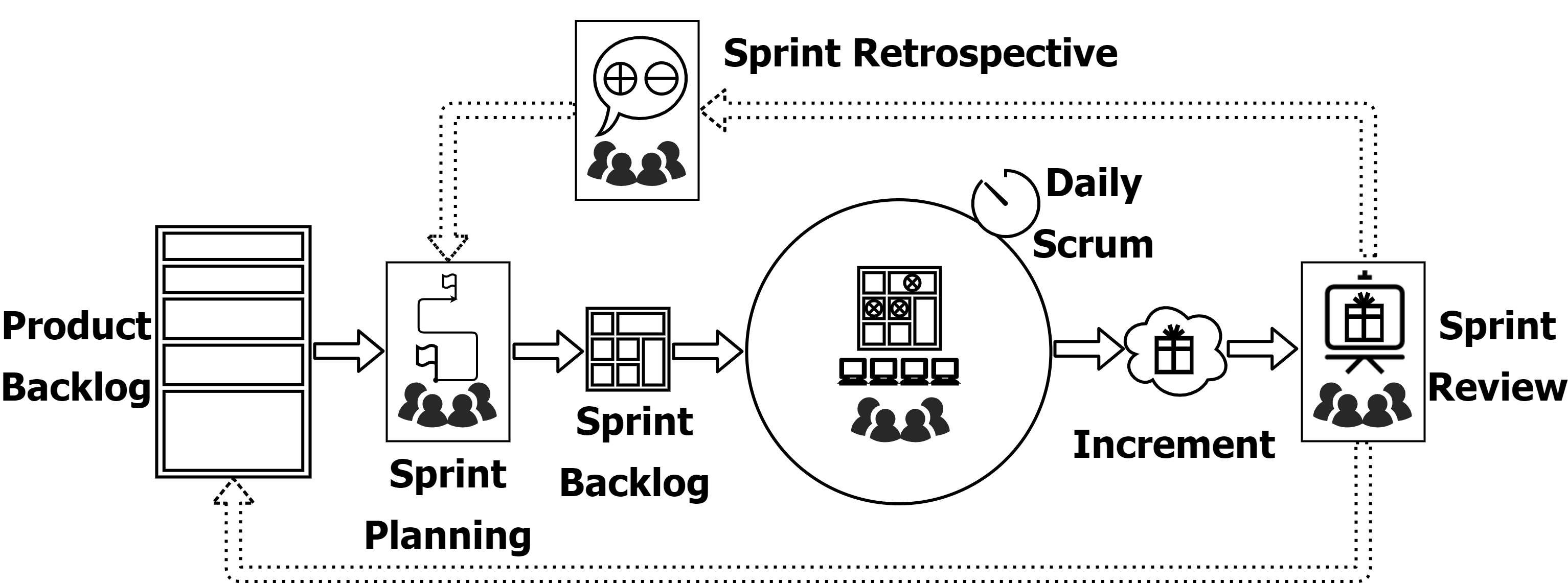
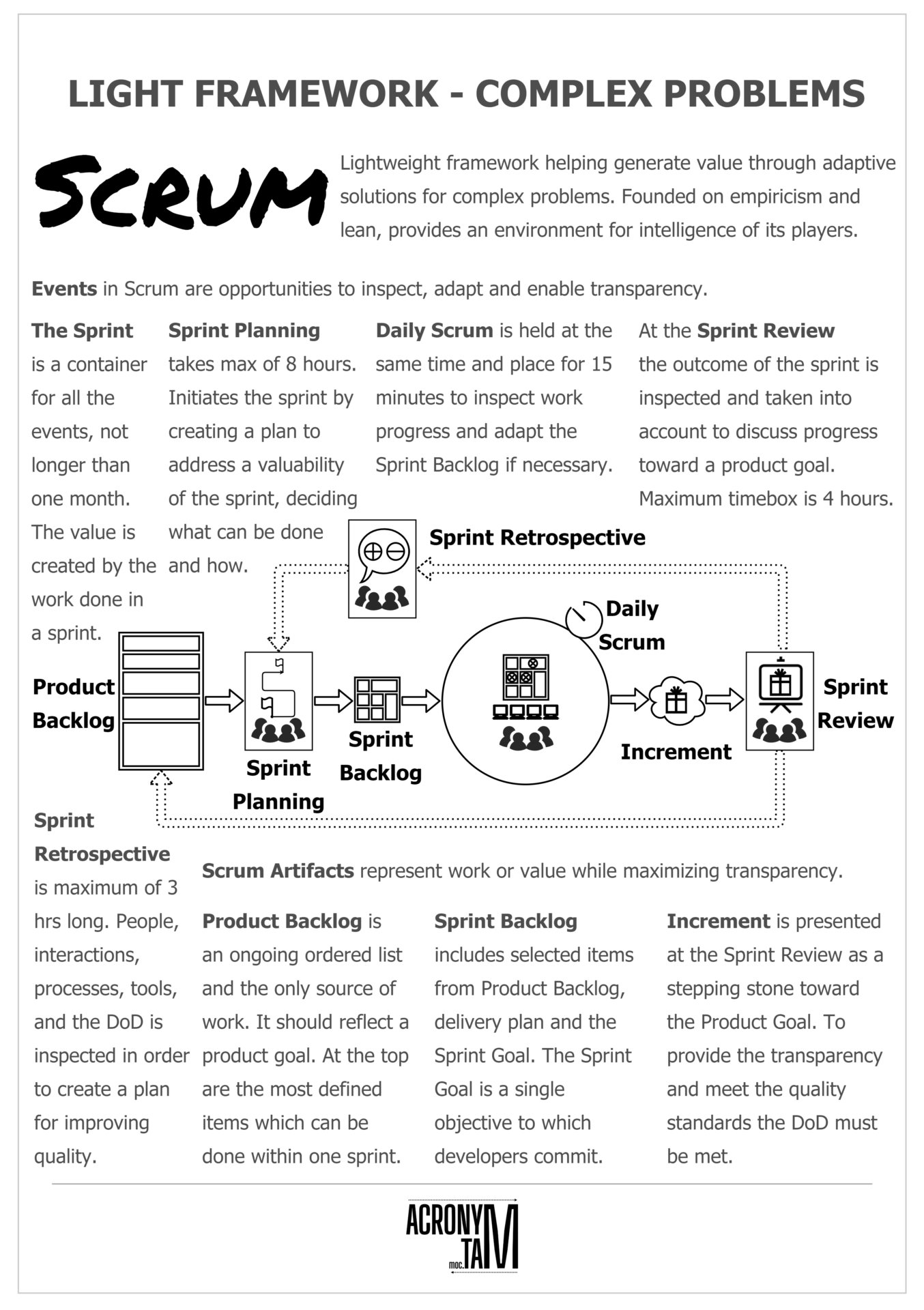
Scrum Events
Events in Scrum are opportunities to inspect, adapt and enable transparency.
The Sprint
A container for all the events, not longer than one month. The value is created by the work done in a sprint.
Sprint Planning
Timeboxed for 8 hours. Initiates the sprint by creating a plan for addressing a valuability of the sprint, deciding what can be done and how.
Daily Scrum
Same time and place for 15 minutes to inspect work progress and adapt the Sprint Backlog if necessary.
Sprint Review
Outcome of the sprint is inspected. The outcome is taken into account and progress toward a product goal is discussed. Maximum timebox is 4 hours for a one-month sprint.
Sprint Retrospective
The maximum of three hours for a one-month sprint. Individuals, interactions, processes, tools, and the Definition of Done is inspected in order to create a plan for improving quality.
Scrum Artifacts
Represent work or value while maximizing transparency.
Product Backlog
An ongoing ordered list, which is the only source of work for the scrum team. It should reflect a product goal. At the top should be the most defined items which can be done within one sprint.
Sprint Backlog
Includes selected items from Product Backlog, plan for delivering them and the Sprint Goal based on which the previous are chosen. The Sprint Goal is a single objective to which developers commit.
Increment
Is presented at the Sprint Review as a stepping stone toward the Product Goal. To provide the transparency and meet the quality standards the Definition of Done must be met.