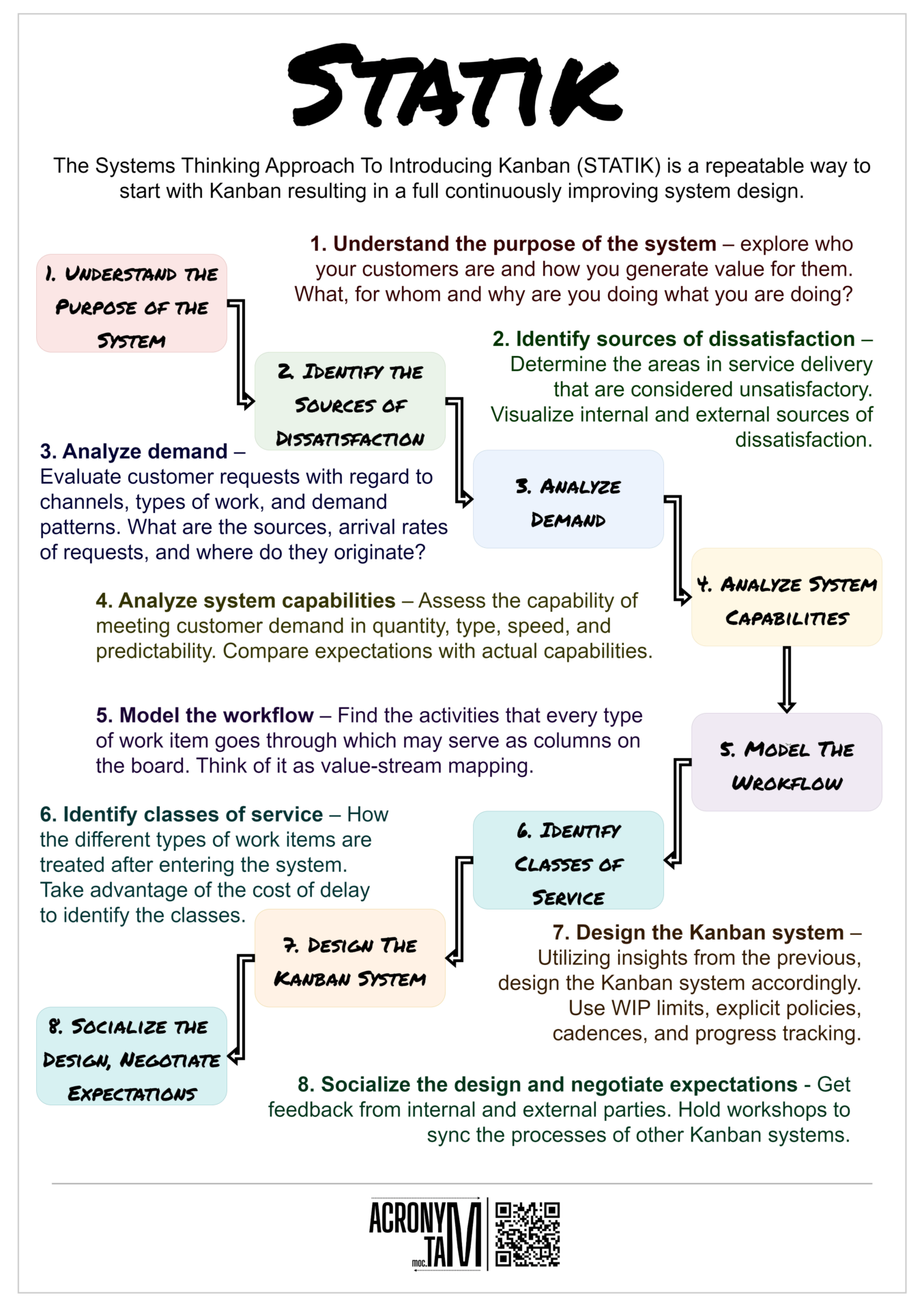
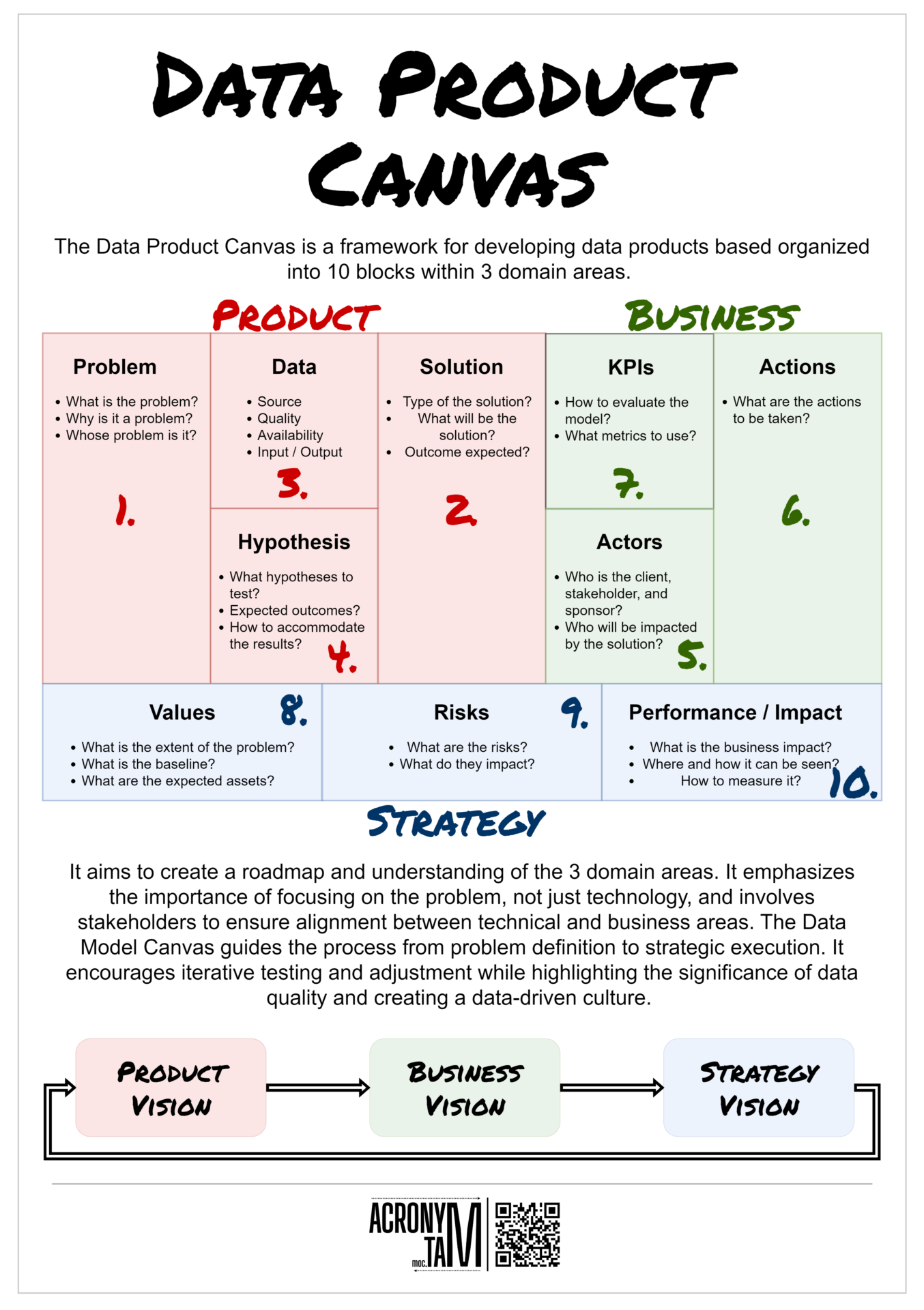
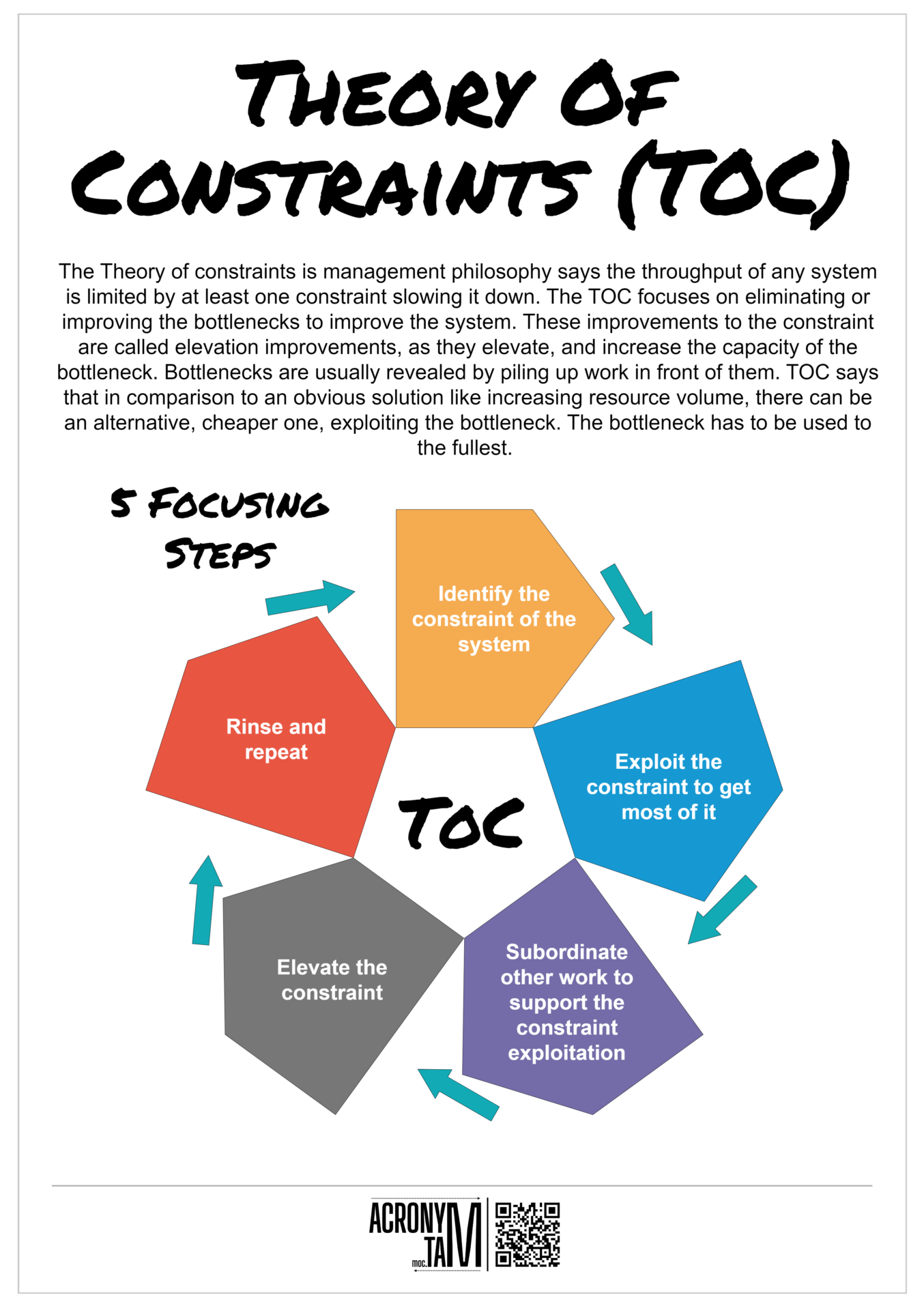
Article
DEEP Product Backlog
Product backlog is an ordered list of the known things that need to be done in a product. The backlog is a living artefact and that is why ensuring that the Product Backlog is DEEP requires regular refining or grooming it.
Detailed Appropriately
Items in the Product Backlog that are on the top should be the more detailed in comparison with the items that are lower. The top ones should be smaller and detailed enough, so they can be completed in the following iteration.
Estimated
Because the Product Backlog is also used for planning, the items at the top should be estimated more accurately compared to the items at lower levels, which are rougher and should be re-estimated as more is known.
Emergent
A Product Backlog is a living artefact, evolving over time. With the progress on the Product the items in the Backlog are added, removed, or rearranged as more is learned.
Prioritized
Priority is based on the value that the items in the Product Backlog brings to the customer. This is the way the Backlog is maximizing value by keeping the highest priority items at the top.